Hormones quietly orchestrate almost every function in your body, from your mood and energy levels to your metabolism and sleep.
Yet, when these powerful chemical messengers fall out of balance, the effects can be surprisingly subtle—and easily overlooked.
Many people dismiss persistent fatigue, unexplained weight changes, or mood swings as “just life,” not realizing these could be signals from their hormones.
Spotting these understated symptoms early is crucial.
The good news? By tuning in to your body and making simple, natural adjustments, you can often restore balance and reclaim your health.
1. Persistent Fatigue
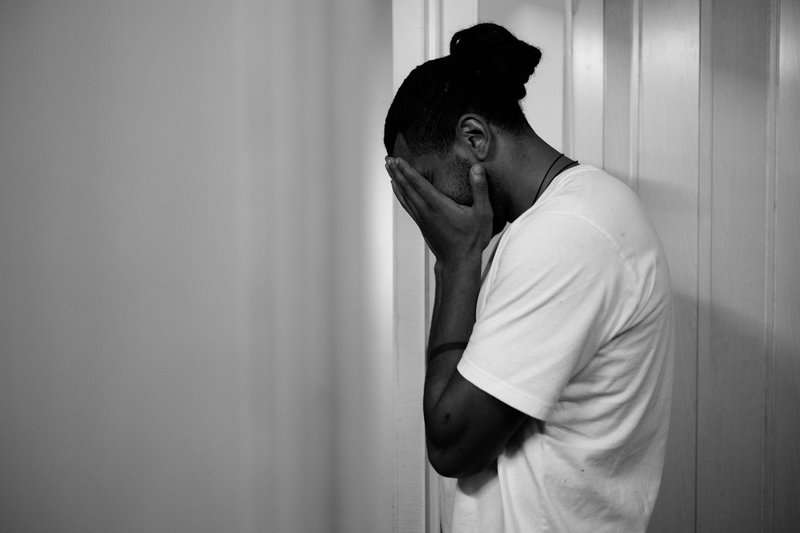

Feeling constantly drained, even after a full night’s sleep, can be a subtle yet telling sign of hormonal imbalance.
Disruptions in thyroid hormones or cortisol—your body’s main stress hormone—often leave you feeling sluggish and unable to recharge.
This kind of unexplained tiredness is sometimes linked to chronic fatigue syndrome, which is frequently associated with hormonal issues.
If your energy doesn’t bounce back despite rest, it’s time to consider your hormones as a possible culprit.
Learn more from Mayo Clinic.
2. Weight Fluctuations

Unexplained weight gain or loss, despite no major changes in diet or exercise, often points to hormonal imbalances.
Issues with thyroid hormones—such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism—can cause your body to gain or lose weight rapidly.
Similarly, imbalances in insulin or cortisol may disrupt how your body stores fat and uses energy.
If your weight is shifting in ways that don’t make sense, your hormones might be the hidden reason.
Read about hormonal weight changes at Cleveland Clinic.
3. Difficulty Sleeping
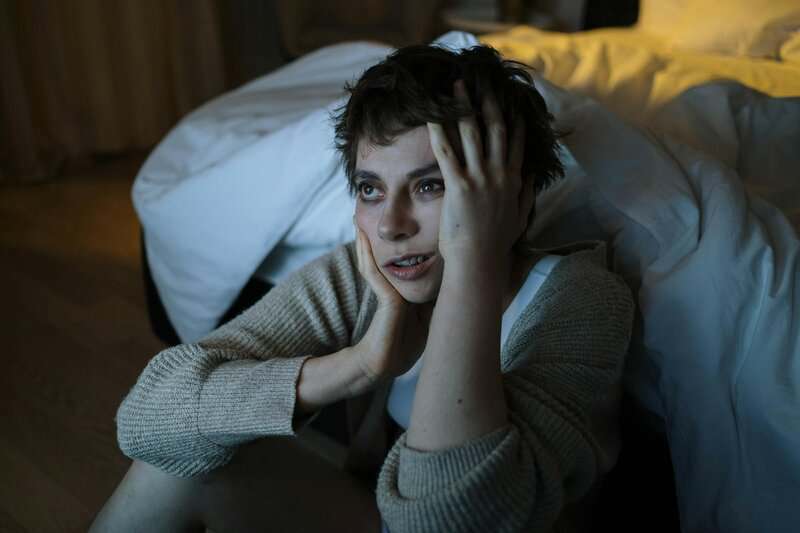

If you’re struggling to fall asleep or waking up frequently during the night, your hormones could be to blame.
Hormones like melatonin and cortisol play a crucial role in regulating your sleep-wake cycle.
Women, in particular, may notice disrupted sleep during times of estrogen fluctuation, such as menstruation or menopause.
Persistent sleep issues may reflect underlying hormonal imbalances that deserve attention.
Harvard Health explains more.
4. Mood Swings and Anxiety
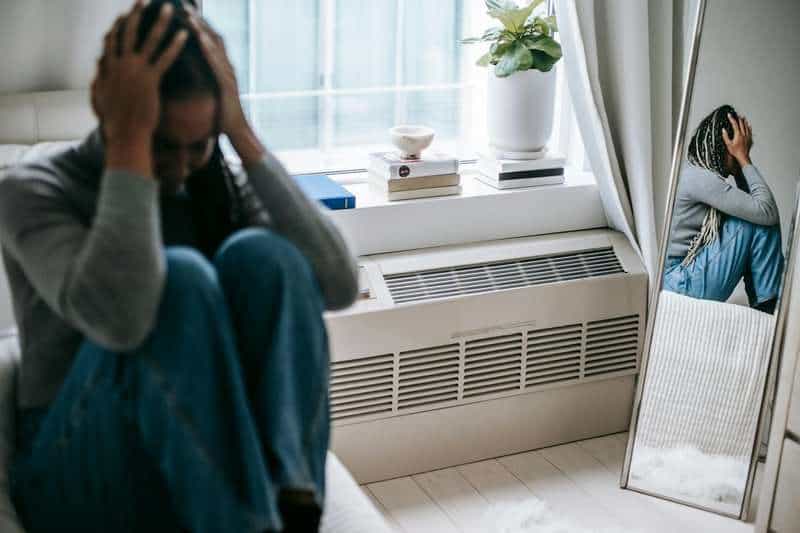

Sudden shifts in mood, unexplained irritability, or heightened anxiety are often tied to hormonal fluctuations.
Imbalances in estrogen, testosterone, or hormones that regulate serotonin can all disrupt emotional stability.
This is especially common during PMS, pregnancy, or menopause, when hormones are in flux.
For both men and women, feeling emotionally unsettled without a clear cause may be your body’s way of signaling a hormonal issue.
Mental Health America discusses this connection.
5. Low Libido

A noticeable decrease in sexual desire can be a subtle sign that your hormones are out of sync.
Low levels of estrogen, testosterone, or progesterone—often during perimenopause or periods of chronic stress—can directly impact libido.
If you find your interest in intimacy fading without an obvious reason, it may be time to explore your hormonal health.
See more from Healthline.
6. Hair Loss or Thinning

Sudden or gradual hair thinning can be a subtle but distressing sign of hormonal imbalance.
Changes in thyroid hormones, androgens, or estrogen levels are common culprits.
Postpartum women often notice increased shedding, while those with thyroid disorders may experience diffuse thinning.
If you see more hair in your brush or on your pillow, your hormones could be the reason.
American Academy of Dermatology offers details.
7. Persistent Acne

Stubborn acne that persists into adulthood—especially along the jawline or chin—can be a clue your hormones are out of balance.
Elevated androgens or issues with insulin regulation can trigger excess oil production, clogging pores and leading to breakouts.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder associated with this type of acne.
If your skin issues don’t respond to typical treatments, it may be worth considering a hormonal evaluation.
For more, see the American Academy of Dermatology.
8. Irregular Periods

Unexpected changes in your menstrual cycle—such as missed periods, unusually heavy bleeding, or cycles that vary in length—can be a direct reflection of hormonal imbalance.
Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone are often to blame, but conditions like PCOS and thyroid disorders can also disrupt normal cycles.
If your periods have become unpredictable or you notice significant changes, it’s wise to explore your hormonal health further.
Learn more at Johns Hopkins Medicine.
9. Digestive Issues
Frequent bloating, constipation, or diarrhea can sometimes be traced back to hormonal imbalances, particularly involving estrogen and cortisol.
When stress hormones rise, digestive function often suffers, leading to uncomfortable symptoms that may seem unrelated to hormones at first glance.
Women may notice digestive changes during hormonal shifts, such as menstruation or menopause.
Understanding the connection can help you address the root cause, not just the symptoms.
Cleveland Clinic explores this link.
10. Brain Fog

Struggling with concentration, forgetfulness, or mental confusion—often described as “brain fog”—may indicate low thyroid hormones or rapidly changing estrogen levels.
These cognitive symptoms are especially common for women in perimenopause but can affect anyone with hormonal imbalance.
If your mind feels cloudy and your memory lapses more frequently, your hormones could be influencing your mental clarity.
The Endocrine Society explains more.
11. Unexplained Sweating or Hot Flashes
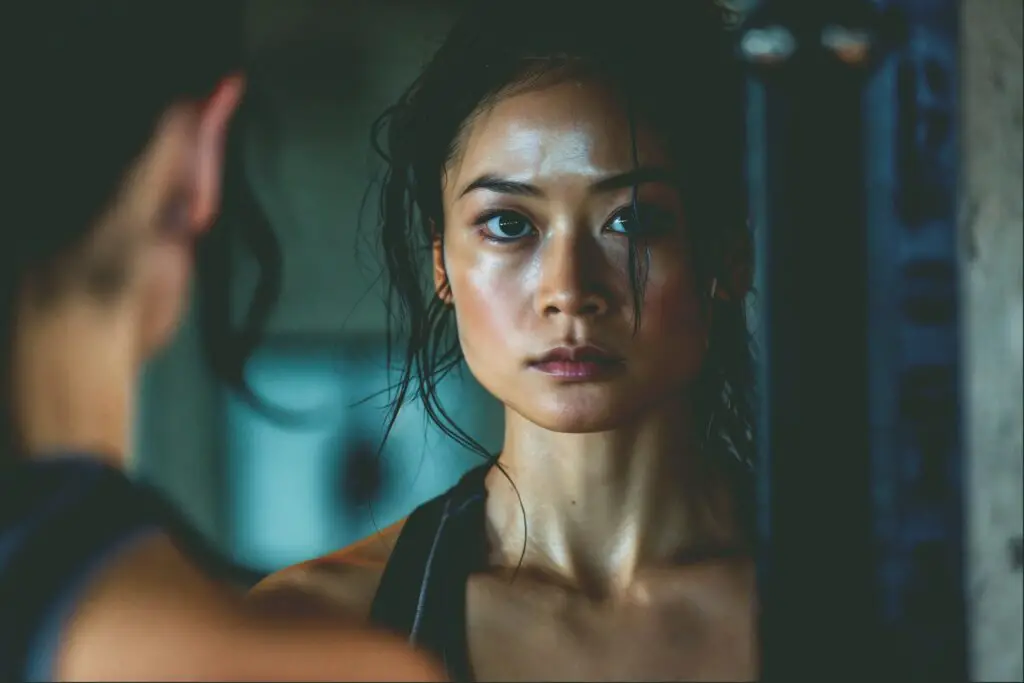

Experiencing sudden bouts of sweating, night sweats, or intense hot flashes can be an obvious signal of hormonal changes in your body.
These symptoms are most commonly linked to menopause, but can also result from thyroid dysfunction in both men and women.
If you notice these episodes without a clear external cause, your hormones may be the underlying reason.
Read more at NHS.
12. Cravings and Appetite Changes
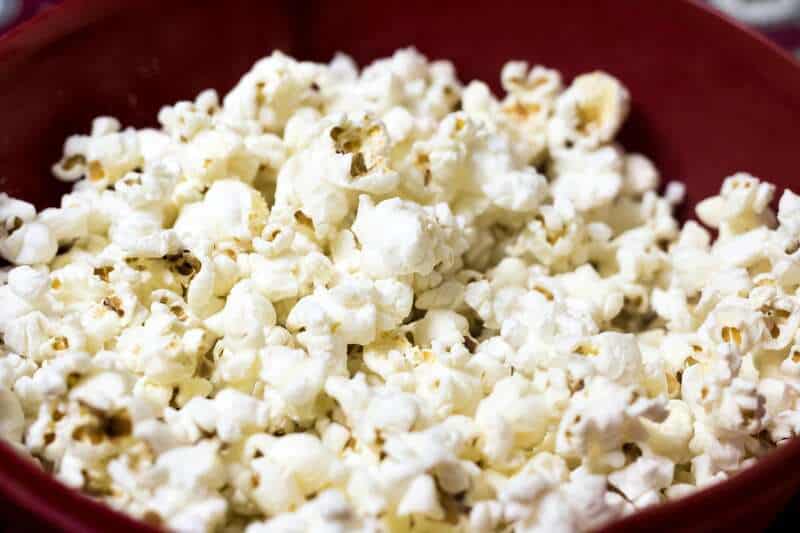

Intense food cravings or sudden shifts in appetite can be a subtle sign of hormonal imbalances, particularly involving insulin, leptin, and cortisol.
Periods of high stress or PMS are frequent triggers, often making you reach for sugary or salty foods.
These changes are your body’s way of signaling that hormones affecting hunger and satiety may be out of sync.
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health offers insights.
Prioritize Sleep Hygiene
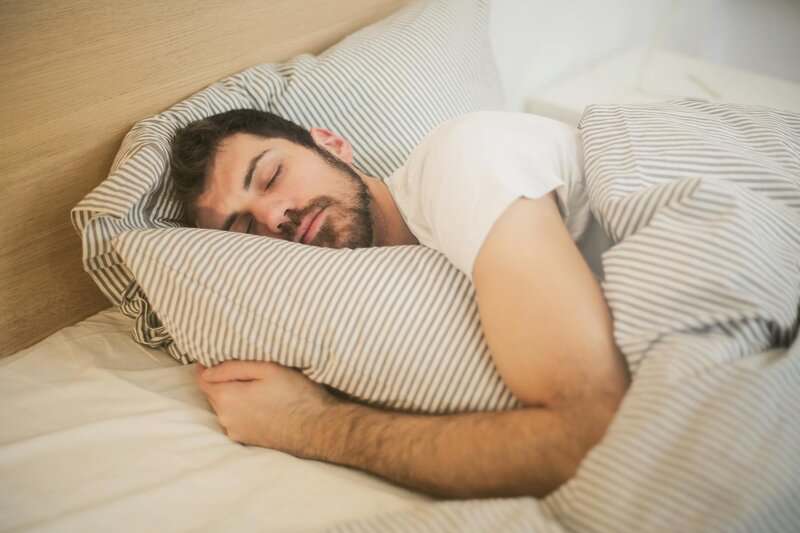

Establishing healthy sleep habits is essential for hormonal balance.
Aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep each night by sticking to a consistent sleep schedule, limiting screen time before bed, and creating a calm, dark environment.
Quality sleep helps regulate key hormones like cortisol, melatonin, and insulin.
Simple changes to your nighttime routine can make a big difference.
CDC sleep tips
Manage Stress Naturally
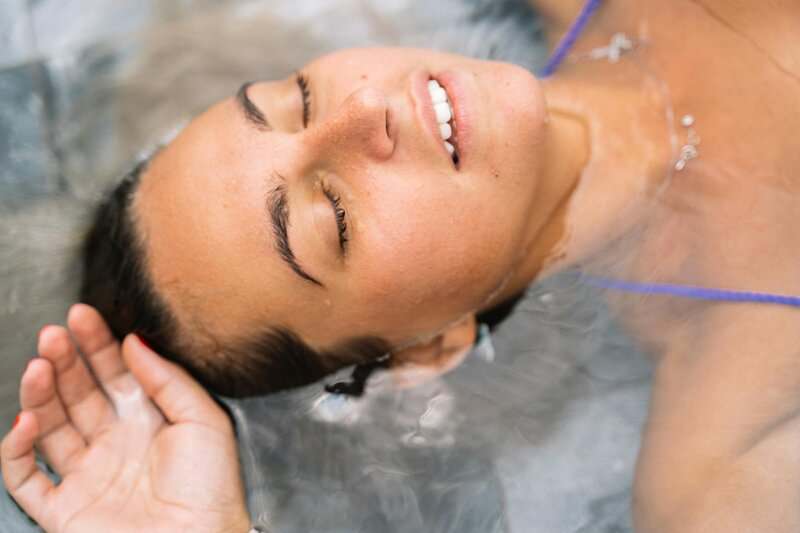

Chronic stress can throw your hormones seriously off-balance, especially cortisol.
Incorporate natural stress-relief techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga into your daily routine.
These practices can help calm your mind, lower cortisol, and restore your body’s equilibrium.
Even a few minutes of mindful breathing each day makes a difference.
Prioritizing stress management is one of the most effective ways to support natural hormone health.
Mayo Clinic on stress management
Eat a Balanced Diet
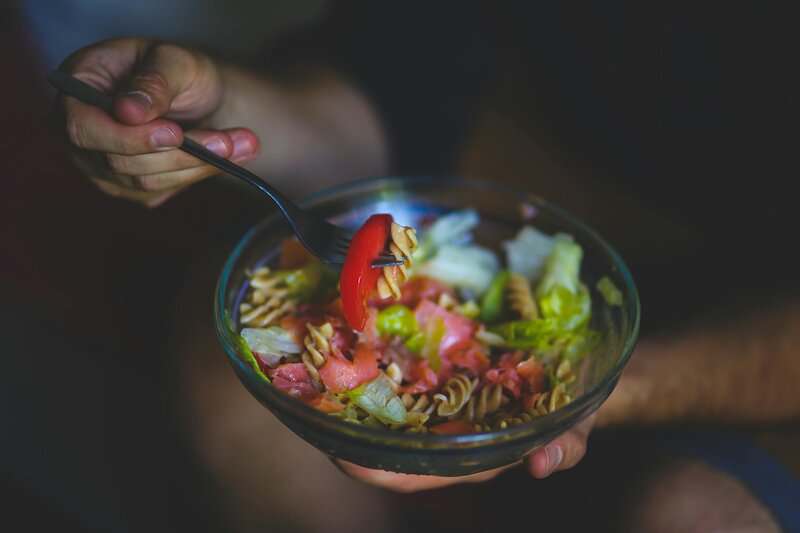

Nourishing your body with whole foods, healthy fats, lean proteins, and plenty of fiber-rich vegetables can help keep your blood sugar and hormone levels steady.
Avoid highly processed foods and added sugars, which can trigger spikes and crashes in hormones like insulin.
Focusing on balanced meals supports overall endocrine health and helps reduce the risk of hormonal imbalances.
For more tips on building healthy eating habits, visit Harvard School of Public Health on healthy eating.
Exercise Regularly
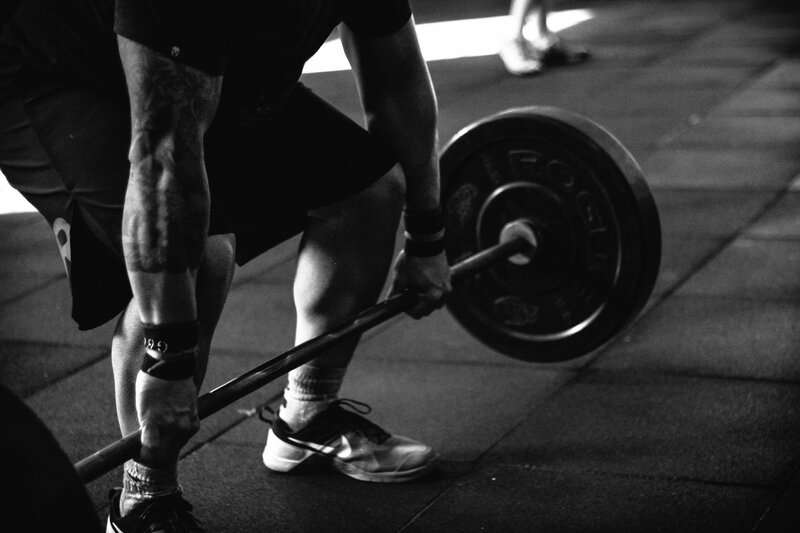

Regular physical activity is a powerful way to support balanced hormones.
Strength training and moderate cardio, in particular, can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone.
Aim for a mix of movement throughout your week to maximize benefits.
Staying active not only boosts mood and energy but also helps keep your endocrine system in check.
See CDC recommendations
Limit Toxin Exposure

Many everyday products contain endocrine disruptors—chemicals that can interfere with your hormonal balance.
Plastics, pesticides, and some personal care items are frequent sources of these toxins.
Choosing glass or stainless steel over plastic, washing produce thoroughly, and opting for clean beauty products can help reduce your exposure.
These small changes can make a meaningful difference in supporting your body’s natural hormone rhythms.
Read about endocrine disruptors from NIEHS
Support Gut Health

A thriving gut microbiome plays a crucial role in hormone regulation and metabolism.
Consuming foods rich in probiotics (like yogurt or fermented vegetables) and prebiotics (such as garlic, onions, and bananas) helps nourish beneficial gut bacteria.
A balanced gut can improve everything from estrogen breakdown to mood and immunity, supporting overall hormonal harmony.
Harvard Medical School on probiotics
Stay Hydrated

Drinking enough water is essential for hormone transport and effective cellular communication.
Proper hydration supports your body’s natural detoxification and keeps hormonal signals flowing smoothly.
Aim for at least 8 cups of water daily, adjusting for activity level and climate.
Making hydration a priority is a simple yet powerful way to help your hormones function at their best.
CDC on hydration
Consider Herbal Remedies

Certain herbs have been traditionally used to support hormonal balance.
Ashwagandha, maca root, and chasteberry are among the most popular, with some evidence suggesting they may help manage stress, regulate cycles, and ease symptoms of imbalance.
However, herbal supplements can interact with medications and may not be suitable for everyone.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new herbal regimen.
See research from the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
Know When to Seek Medical Advice

Sometimes, natural approaches alone aren’t enough.
If your symptoms persist, worsen, or significantly impact your daily life, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional.
Blood tests and a thorough medical evaluation can help identify specific hormonal imbalances and guide targeted treatment.
A doctor can also rule out underlying conditions that may require more specialized care.
Don’t hesitate to seek support when needed—early intervention can make a meaningful difference.
Endocrine Society guidance
Disclaimer

This article is for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Always consult your physician or a qualified health provider with any questions about a medical condition or your hormonal health.
Your wellbeing is unique—seek personalized guidance when making health decisions.



Vielleicht interessiert es Sie:
13 Extraordinary Giants Ready to Blow Your Mind! 🌍
10 Chonky Oddities That Will Leave You Speechless! 🤯
9 Unbelievable Absolute Units That Will Leave You Speechless! 🌟
10 Colossal Creatures That Will Leave You Speechless! 🐻
12 Shocking Absolute Units You’ll Have to See! 😲
12 Epic Absolute Units That Will Challenge Your Perceptions! 🔥
Uncover the 11 Ultimate Massive Oddities That Awe! 🌍
9 Unbelievable Oddities That Redefine ‚Massive‘! 🐉💎