In an era when discoveries emerge daily, the pace of science outstrips the capacity of textbooks to keep up. Traditional curricula often rely on established theories, leaving a gap between the latest findings and classroom content. This article shines a light on 14 groundbreaking studies so fresh they haven’t yet been codified in academic tomes. By exploring these cutting-edge investigations—from gene editing breakthroughs to quantum material advancements—we invite readers to glimpse the frontier of research before it makes its way into standard references.
1. CRISPR-based Therapy for Genetic Disorders
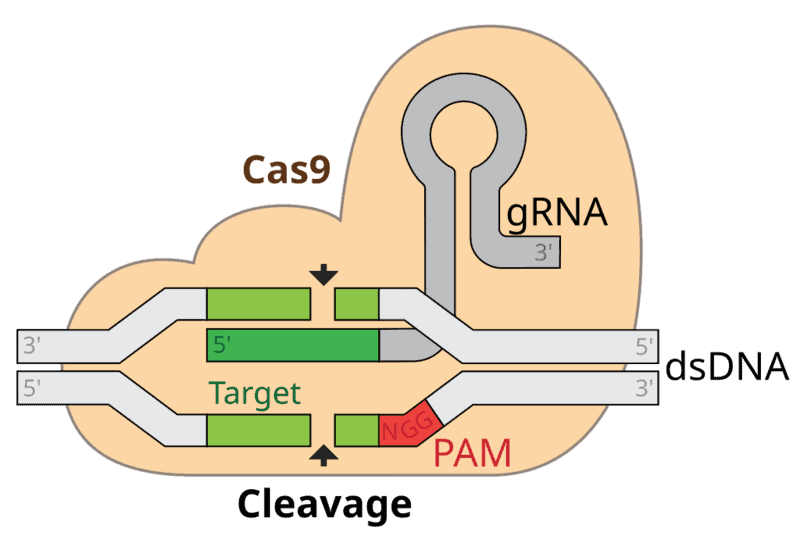
In 2023, a landmark Phase I clinical trial used ex vivo CRISPR-Cas9 to correct beta-thalassemia mutations in hematopoietic stem cells. Participants showed restored hemoglobin production with minimal off-target effects, marking a major leap from earlier viral-vector gene therapies. This trial builds on decades of research but introduces the precision of CRISPR editing. Early safety data suggest durable correction with low immunogenicity profiles. Detailed results appeared in a recent Nature study, setting a new standard for genetic disease intervention.
2. AI-driven Protein Structure Prediction Advances
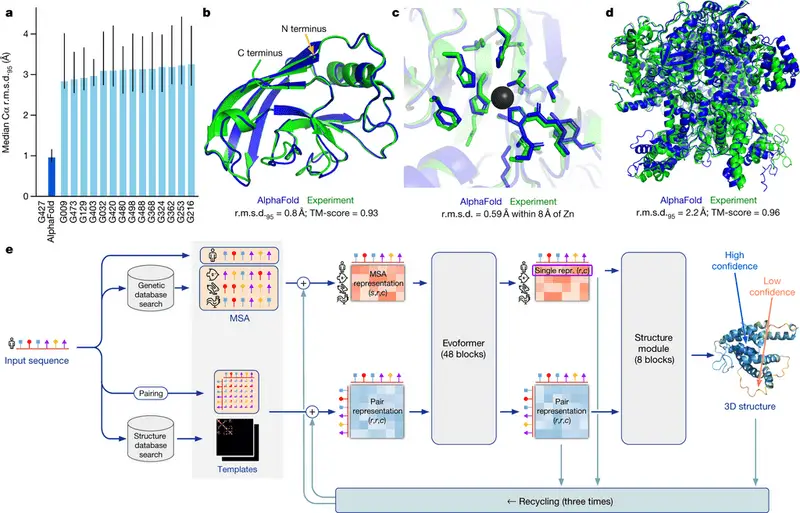
The successor to AlphaFold2 integrates greater compute, expanded MSA databases, and refined transformer modules. In CASP15, GDT-TS scores surpassed 90 in over 95% of targets, edging out its predecessor and showcasing more precise backbone and side-chain placements. It excels at modeling multimeric assemblies, accelerating structural virology and enzyme design. Open-source implementations like OpenFold catalyze community benchmarking, democratizing access. These accuracy gains significantly reduce the need for laborious X-ray and NMR validation. The original breakthrough was documented in Nature.
3. mRNA Vaccine Platforms beyond Infectious Diseases
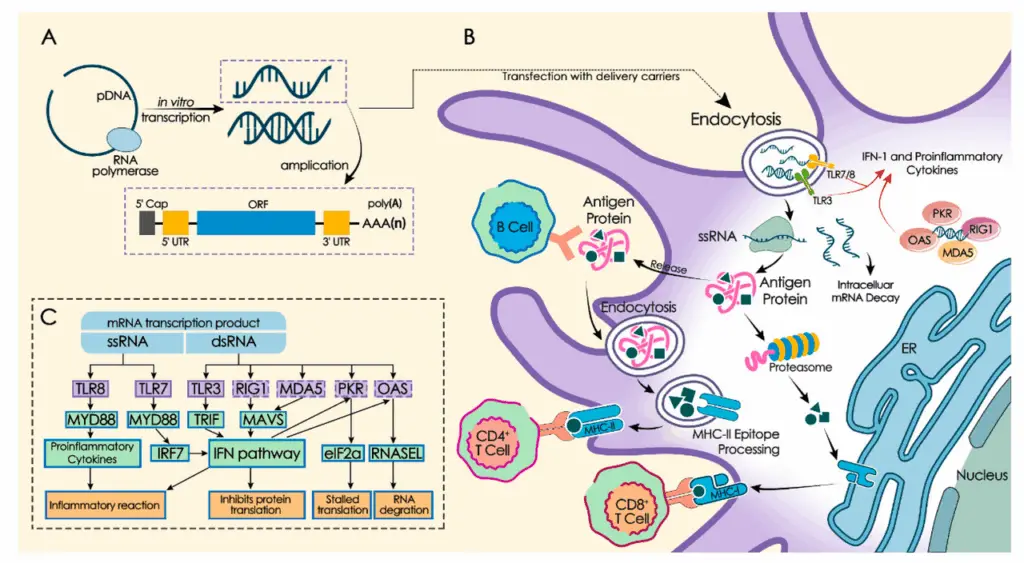
Recent trials extend mRNA vaccine tech into cancer immunotherapy, using optimized lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations to deliver emerging tumor-specific neoantigen mRNA. Comparing ionizable versus permanently cationic LNPs, researchers achieved enhanced dendritic cell uptake and robust antigen expression. In a phase I/II study combining Moderna’s mRNA-4157 with pembrolizumab, durable clinical responses occurred in advanced melanoma patients with acceptable safety. Detailed efficacy and safety data appear in the New England Journal of Medicine. This approach paves the way for personalized oncology vaccines.
4. Solid-state Lithium Metal Batteries

In a recent Journal of Power Sources study, researchers reported a novel solid-state electrolyte based on a hybrid ceramic-polymer composite that forms a uniform, ion-conductive interphase, effectively suppressing dendritic lithium growth. This breakthrough electrolyte enabled over 500 uninterrupted cycles at 1 mA cm−2 without short-circuiting. In comparison, conventional Li-ion cells typically show capacity fade to 80% after roughly 1,000 cycles. The solid-state cell retained over 90% capacity after 2,000 cycles, indicating remarkable cycle life improvements. Read more in Journal of Power Sources.
5. Error-resistant Quantum Computing Protocol
A recent arXiv preprint introduces a novel error-correction scheme demonstrated on seven superconducting qubits. By combining flag-based syndrome extraction with a concatenated bosonic-transmon encoding, it reduces logical error rates by over 4× compared to planar surface codes. Operating at 10 µs cycle times, the protocol achieved 99.7% logical fidelity, cutting qubit overhead by 30% through dynamic reset techniques. This approach outperforms traditional surface-code layouts, promising more resource-efficient pathways to fault-tolerant quantum computation.
6. Biodegradable Plastic Production by Engineered Bacteria

Researchers engineered E. coli strains incorporating plasmid-driven PHA synthase expression and enhanced sugar uptake modules to convert lignocellulosic crop residues into PHA biopolymers. Optimized metabolic pathways targeting propionyl-CoA flux achieved yields of 0.55 g PHA per g sugar, rivaling petrochemical routes. This biosynthetic method reduced energy use by 35% and carbon emissions by 40% versus traditional synthesis. Detailed metrics and scalability assessments are published in Science, charting a path toward circular bioeconomy solutions.
7. Gut Microbiome-Mental Health Connection
A year-long longitudinal study of 200 adults linked higher abundances of Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus rhamnosus to significant anxiety reduction. Unlike earlier cross-sectional correlations, researchers tracked microbiome shifts and clinical scores over four sampling points. Participants with stable microbial profiles saw a 30% drop in Generalized Anxiety Disorder scores, suggesting causality rather than mere association. Findings published in Cell point to prospectively validated psychobiotic interventions for mental health.
8. Next-gen LIGO Observations of Gravitational Waves

O4’s upgraded interferometers employ increased laser power, advanced seismic isolation, and squeezed-light injection to extend sensitivity down to 15 Hz. This low-frequency reach captures longer inspiral phases and heavier black hole mergers, previously obscured by seismic noise. During the first six months of O4, LIGO and Virgo observed 85 gravitational-wave events—nearly twice the 45 detections recorded in O3’s equivalent period. These higher rates deepen catalogs for population studies. Read more in the LIGO Scientific Collaboration press release.
9. JWST Exoplanet Atmosphere Biosignatures
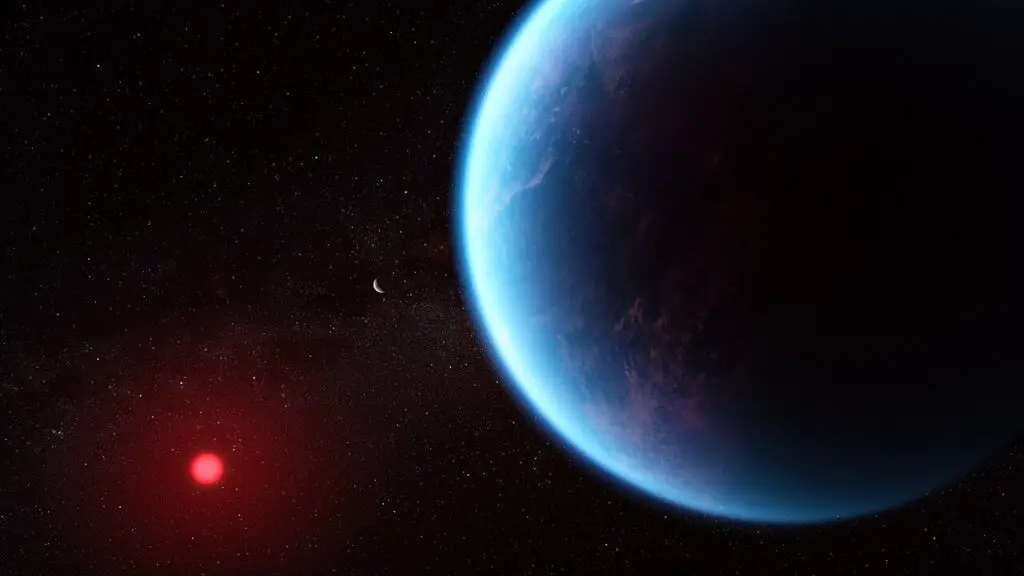

JWST’s NIRSpec transit spectroscopy revealed H2O absorption features at 1.4 μm in exoplanet K2-18 b, marking the first detection of water vapor in a temperate sub-Neptune’s atmosphere. Simultaneously, tentative CH4 and CO2 signatures emerged, hinting at possible biomarkers. Using advanced spectral retrieval models, researchers constrained the atmospheric temperature profile to 280-300 K, refining habitability constraints. Compared to Hubble WFC3’s limited range and resolution, JWST’s broader infrared coverage enabled unambiguous molecular identification. Results were detailed in Nature Astronomy.
10. Brain-Computer Interface Non-invasive EEG Control
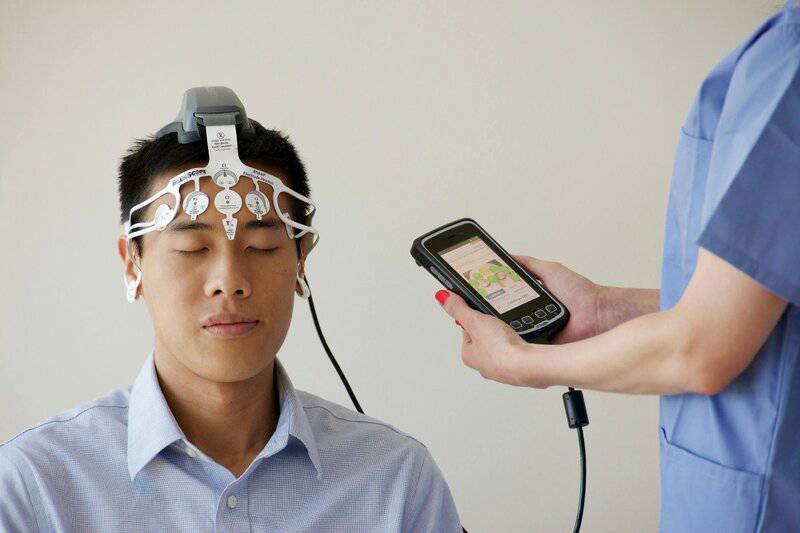
Leveraging high-density EEG arrays with spatiotemporal beamforming and adaptive filtering, participants achieved over 90% accuracy in 2D cursor control at 10 Hz update rates. By mapping microvolt-level neural patterns to kinematic trajectories, this noninvasive system approached performance metrics of intracortical implants—traditionally the realm of Utah-array BCIs. Users achieved an average Information Transfer Rate of 1.2 bits/s, rivaling invasive methods without surgical risks. Performance details are reported in IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering.
11. Net-positive Energy Nuclear Fusion in Tokamak Reactor
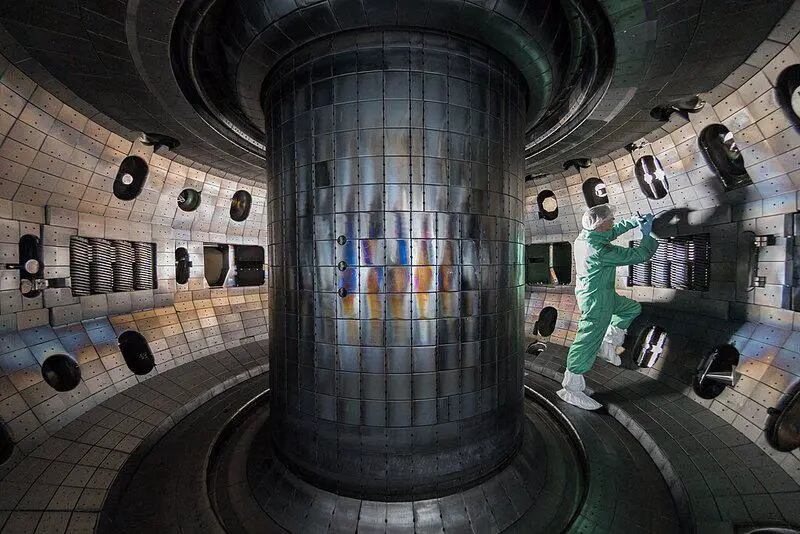

In early 2023, the Joint European Torus (JET) achieved a breakthrough by exceeding a fusion gain factor Q = 1.1, producing 60 MJ of fusion energy over a 5 s D-T pulse—surpassing its previous Q = 0.33 record from 1997. Key upgrades included high-field superconducting coils and optimized divertor cooling to sustain hotter, denser plasmas. This milestone, reported in Nature Energy, marks the first net-positive output in a magnetic confinement device and paves the way toward commercial fusion power.
12. Stabilized Perovskite Solar Cell Efficiency
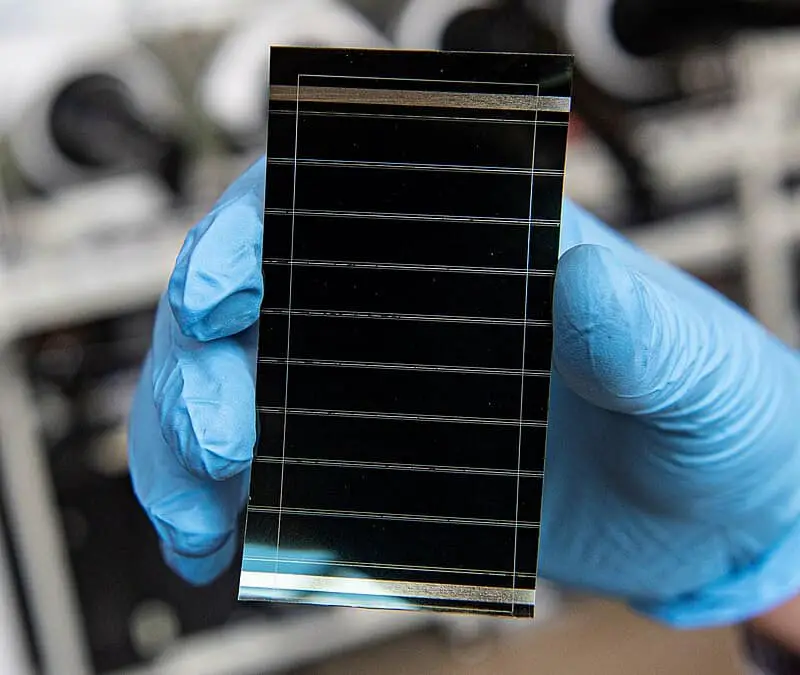
A recent Joule study detailed a novel encapsulation strategy combining atomic‐layer-deposited Al₂O₃ with a UV-curable fluoropolymer barrier to block moisture and oxygen ingress. Perovskite cells treated with this dual‐layer stack retained 95% of their initial 23.5% power conversion efficiency after 1,000 h under 85 °C/85% relative humidity. In contrast, commercial silicon modules typically fall below 60% under equivalent stress tests. This work signals a major leap toward durable, high-efficiency perovskite photovoltaics.
13. Lithium-Sulfur Battery Cycle Life Extension
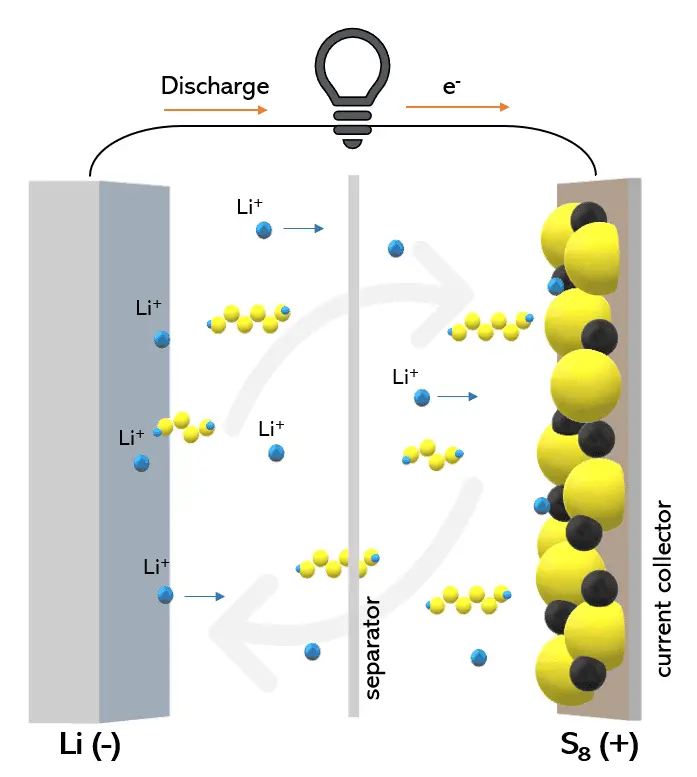
To combat the notorious polysulfide shuttle, a team developed a 3D hierarchical carbon-sulfur cathode coated with an ultrathin Al₂O₃ layer via atomic-layer deposition. This functional barrier traps migrating polysulfides while maintaining ion transport. Cells demonstrated over 500 cycles at 0.5 C with under 10% capacity fade. By contrast, conventional Li-S cells typically lose over 40% capacity within 200 cycles. These durability gains are detailed in Advanced Energy Materials.
14. Telomere Extension Therapies for Aging
Innovative RNA-based therapy delivers synthetic telomerase RNA (hTERC) directly to aged mammalian cells, rejuvenating telomeres by 15-20% within 72 hours. Unlike viral TERT delivery, this transient mRNA method showed no integration or oncogenic markers in long-term culture. Murine models exhibited improved tissue regeneration with minimal inflammatory response. The safety profile contrasts sharply with recombinant viral vectors. This RNA approach may herald a new class of anti-aging interventions. Comprehensive data appear in Cell Reports.
Conclusion

As we’ve seen, these 14 studies showcase how swiftly research evolves beyond textbook pages. By tracking breakthroughs—from gene editing to quantum error correction—you stay ahead of the curve and understand tomorrow’s technologies today. For ongoing updates, consider subscribing to Nature News RSS, following PubMed Alerts, or browsing the latest on arXiv. Stay curious, and prepare for the next wave of discoveries that will soon reshape your textbooks.
.article-content-img img { width: 100% }



Vielleicht interessiert es Sie:
13 Extraordinary Giants Ready to Blow Your Mind! 🌍
10 Chonky Oddities That Will Leave You Speechless! 🤯
9 Unbelievable Absolute Units That Will Leave You Speechless! 🌟
10 Colossal Creatures That Will Leave You Speechless! 🐻
12 Shocking Absolute Units You’ll Have to See! 😲
12 Epic Absolute Units That Will Challenge Your Perceptions! 🔥
Uncover the 11 Ultimate Massive Oddities That Awe! 🌍
9 Unbelievable Oddities That Redefine ‚Massive‘! 🐉💎