Falling in love isn’t just a matter of the heart—it’s a profound transformation within your brain. When you fall in love, a cascade of neurochemical changes begins, affecting everything from your mood to your perception of the world.Scientific research reveals that love sparks intense neural activity, shifts the way emotions are processed, and even alters cognitive patterns. This is why the experience can feel so exhilarating, consuming, and sometimes overwhelming. By exploring what truly happens in your brain, we can better understand the magic—and the science—behind falling in love.
1. Dopamine Levels Surge
One of the first things that happens when you fall in love is a dramatic increase in dopamine, the brain’s “feel-good” chemical.
This neurotransmitter is closely linked to pleasure and reward, fueling a sense of euphoria and heightened energy.
You might find yourself thinking about your partner constantly, almost as if you’re addicted.
According to Harvard Medical School, this dopamine rush is what makes those early days of love feel so intense—and so unforgettable.
2. Oxytocin Floods the System
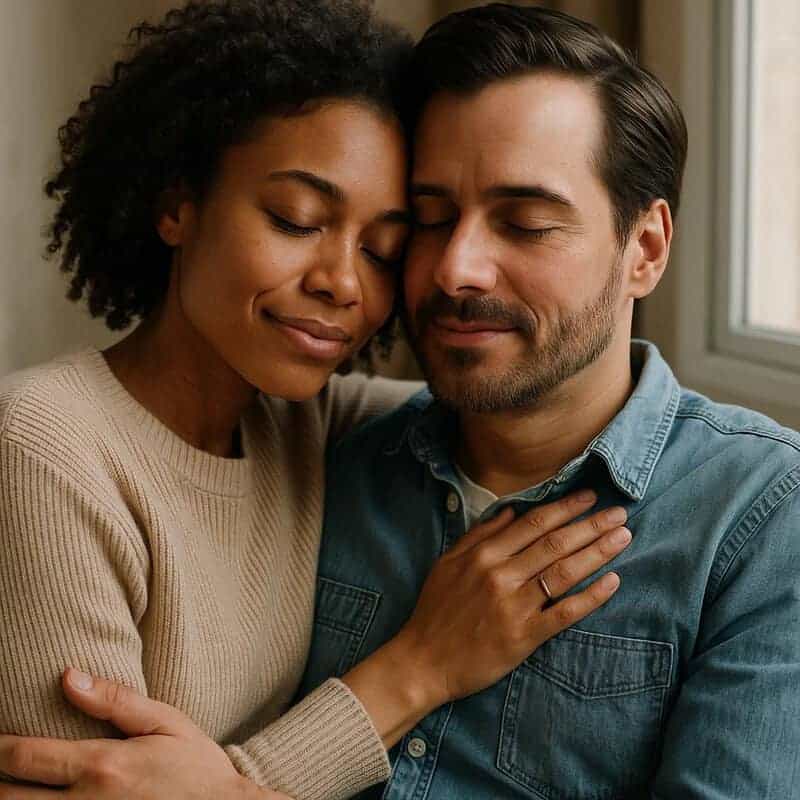

Oxytocin, often called the “cuddle hormone,” plays a crucial role in creating feelings of trust and deep connection.
When you engage in affectionate touch or share intimate moments, your brain releases oxytocin, strengthening the bond between you and your partner.
This hormone is vital for nurturing emotional closeness and sustaining long-term relationships.
As noted by the Cleveland Clinic, oxytocin is at the heart of love’s lasting power.
3. Serotonin Levels Fluctuate
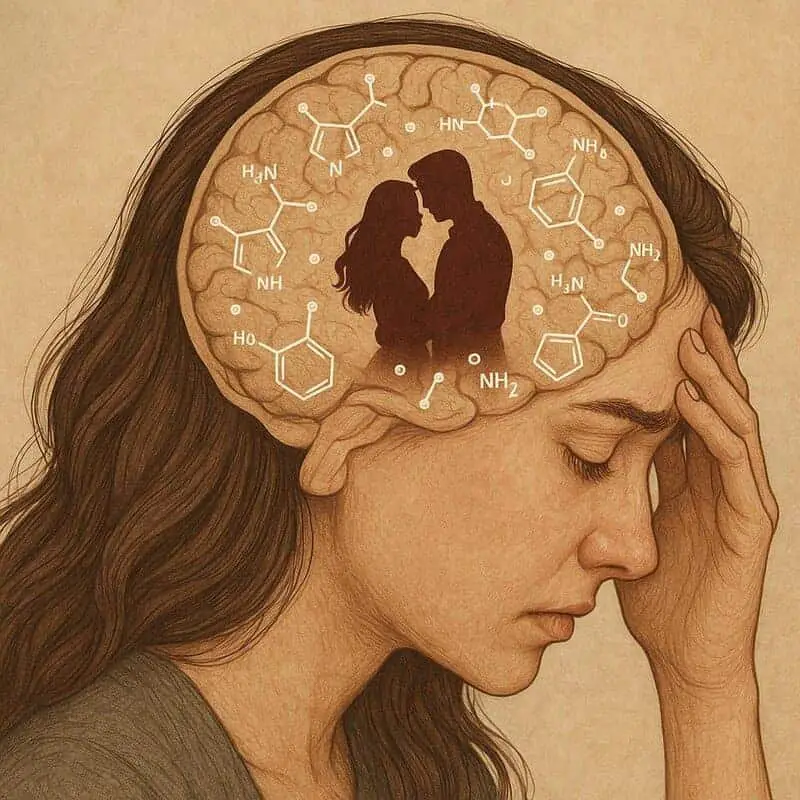

When you fall in love, your serotonin levels can actually drop, leading to constant thoughts and fantasies about your partner.
This decrease is similar to what’s seen in people with obsessive-compulsive tendencies, explaining why new lovers often become so preoccupied.
The mind becomes fixated, making it hard to concentrate on anything else.
According to Scientific American, these serotonin changes are key to understanding love’s all-consuming nature.
4. Stress Response Changes

Love brings a unique blend of excitement and anxiety.
At first, your brain may release more cortisol, the stress hormone, causing those unmistakable jitters or butterflies in your stomach.
However, as relationships mature and stabilize, cortisol levels typically decrease, helping you feel calmer and more secure.
Healthy partnerships can even boost your overall resilience to stress.
The American Psychological Association highlights how love’s evolution profoundly shapes our stress response and overall sense of well-being.
5. Prefrontal Cortex Activity Shifts

The prefrontal cortex is the area of the brain responsible for rational thinking, decision-making, and judgment.
When you fall in love, activity in this region may decrease, making you more impulsive and less likely to notice flaws in your partner.
This neural change helps explain why love can make people overlook red flags or behave in uncharacteristic ways.
The National Institutes of Health explores how these shifts affect our perceptions and choices.
6. Increased Empathy

Falling in love often leads to heightened empathy.
Brain regions involved in understanding and sharing emotions become more active, making it easier to tune into your partner’s feelings.
This neural boost helps couples respond with compassion and emotional support.
According to Frontiers in Psychology, empathy is essential for deepening romantic connections and fostering lasting bonds.
7. Heightened Attention and Focus

When you’re in love, your brain’s reward system directs attention almost exclusively toward your partner.
This intense focus can make them seem like the center of your universe, strengthening emotional connection.
However, it can also mean you’re more easily distracted from daily responsibilities.
As BBC Science Focus notes, this laser-like attention is one of love’s most captivating effects.
8. Emotional Memory Strengthens

Love makes memories more vivid and lasting by boosting activity in the hippocampus and amygdala—areas that process emotion and memory.
Moments like your first date or shared laughter become deeply etched in your mind, often replaying with remarkable clarity.
This is why romantic memories tend to be so powerful and enduring.
As Psychology Today explains, love enhances the brain’s ability to store emotional moments.
9. Risk-Taking Behavior Increases

When you fall in love, inhibitions often drop, making you more likely to take bold steps or make daring gestures.
This increase in risk-taking is driven by changes in brain regions that govern caution and self-control.
As a result, people might pursue new relationships or express feelings more openly.
Live Science explores the neural drives behind these courageous acts.
10. Pain Perception Diminishes

Love has the remarkable ability to reduce physical pain.
Emotional connection and affectionate touch trigger the release of endorphins and oxytocin, which can ease discomfort.
Even something as simple as holding a partner’s hand can provide relief.
Research from Stanford Medicine shows that love can literally make life’s pains feel lighter.
11. Sense of Reward Intensifies

Falling in love supercharges the brain’s reward system, making even simple gestures—like a smile or text—feel incredibly gratifying.
This heightened sense of pleasure fuels the desire to be close and to seek out more shared moments.
The brain essentially teaches you to crave your partner’s presence.
The Guardian discusses how these powerful reward mechanisms keep love so captivating.
12. Motivation Gets a Boost

Love doesn’t just feel good—it makes you more motivated.
The brain’s reward and goal-oriented centers light up, driving you to pursue activities that foster connection and intimacy.
This boost in motivation might lead to planning dates, making thoughtful gestures, or working toward shared goals.
According to The Atlantic, love enhances drive and determination, fueling relationship growth and personal ambition.
13. Self-Concept May Shift

In love, your self-concept can evolve as you begin to see yourself through the lens of your relationship.
People often adopt interests, habits, or perspectives from their partner, subtly reshaping their identity.
This blending of selves can deepen intimacy and understanding.
Research from the National Library of Medicine highlights how romantic bonds actively influence self-perception and growth.
14. Anxiety and Excitement Coexist

Falling in love is often a rollercoaster of emotions, where excitement and anxiety intertwine.
Adrenaline and norepinephrine flood the brain, amplifying arousal, anticipation, and a bit of nervous energy.
This emotional mix makes early romance thrilling yet sometimes overwhelming.
As Verywell Mind notes, it’s this blend that gives new love its unforgettable intensity.
15. Long-Term Attachment Systems Activate

As romantic love matures, the brain transitions from passion to deep attachment.
Regions abundant in oxytocin and vasopressin become more active, fostering feelings of security, trust, and long-term commitment.
These neural pathways are similar to those involved in parent-child bonding, ensuring stability and partnership.
Smithsonian Magazine explores how lasting love is supported by these powerful biological systems, making enduring relationships possible.
Conclusion
Falling in love is truly a transformative experience—not just emotionally, but biologically as well. The brain undergoes remarkable changes, from chemical surges and heightened focus to shifts in memory, motivation, and attachment.These neurological responses help explain why love feels so intense and shapes so many aspects of our lives. As science continues to reveal more, we gain a deeper appreciation for love’s complexity. Embrace these changes and celebrate how love can enrich your mind, your relationships, and your entire world.
.article-content-img img { width: 100% }



Vielleicht interessiert es Sie:
13 Extraordinary Giants Ready to Blow Your Mind! 🌍
10 Chonky Oddities That Will Leave You Speechless! 🤯
9 Unbelievable Absolute Units That Will Leave You Speechless! 🌟
10 Colossal Creatures That Will Leave You Speechless! 🐻
12 Shocking Absolute Units You’ll Have to See! 😲
12 Epic Absolute Units That Will Challenge Your Perceptions! 🔥
Uncover the 11 Ultimate Massive Oddities That Awe! 🌍
9 Unbelievable Oddities That Redefine ‚Massive‘! 🐉💎