The Arctic, once shrouded in ice and mystery, is entering an unprecedented era of discovery.
Rapid warming has accelerated the melting of ancient glaciers, revealing vast expanses of untapped mineral wealth and scientific wonders hidden beneath the ice.
This transformation is not just a natural phenomenon—it’s a catalyst for a new gold rush, driven by technological innovation and intense geopolitical competition.
As nations and companies race to claim their share, the Arctic stands at the crossroads of opportunity and challenge, its secrets gradually coming into the light for the world to see.
1. NOAA’s Ambitious Arctic Mapping Initiative
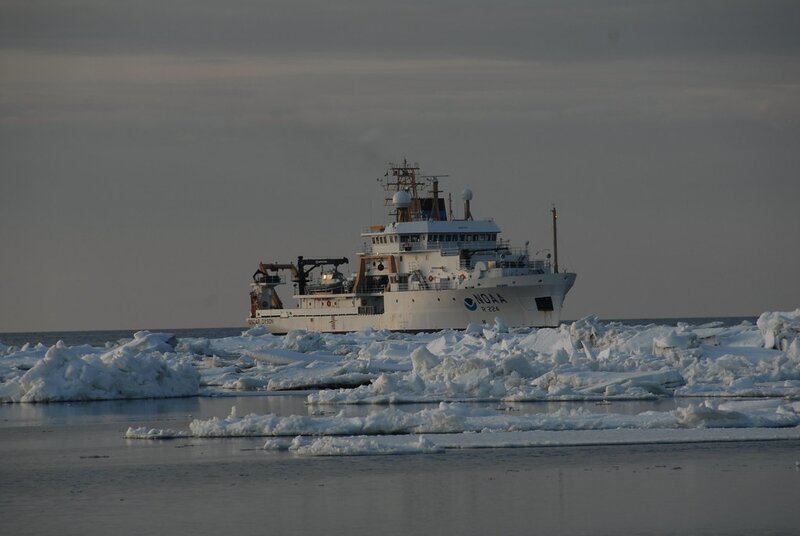

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has unveiled a bold plan to map Alaska’s vast and dynamic Arctic coastal zone by 2030 and its entire exclusive economic zone by 2040.
This initiative will harness advanced technology, including the upcoming NOAA Ship Surveyor and NOAA Ship Navigator, slated to launch in 2027 and 2028.
By filling critical gaps in our understanding of Arctic waters, NOAA’s project will serve as a crucial foundation for safe navigation, resource management, and scientific inquiry.
For more details, see the NOAA Arctic Vision and Strategy.
2. Alaska’s Uncharted Seafloor
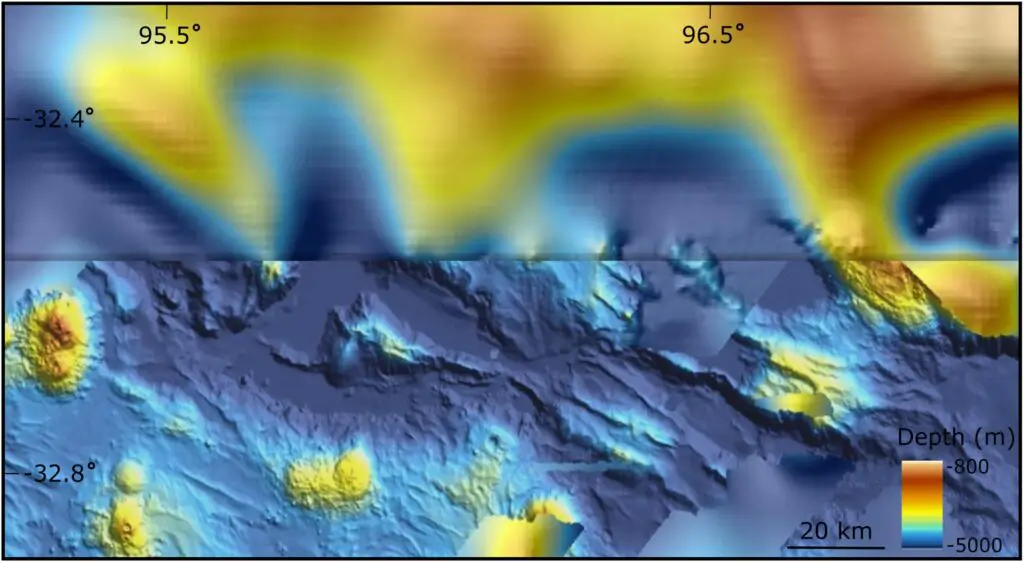
Despite mounting interest, only 38% of Alaska’s seafloor has been mapped as of January 2025.
This leaves immense swaths of the Arctic ocean floor as one of the world’s last scientific frontiers, teeming with unknowns in geology, biology, and hidden resources.
Researchers anticipate that these unexplored depths may yield breakthrough discoveries—from rare minerals to unique ecosystems.
The region’s scientific secrets remain tantalizingly out of reach, awaiting new expeditions to illuminate the mysteries beneath the waves.
Learn more at NOAA Ocean Exploration 2025 Expeditions.
3. 3D Mapping: Multibeam Echo Sounder Breakthroughs
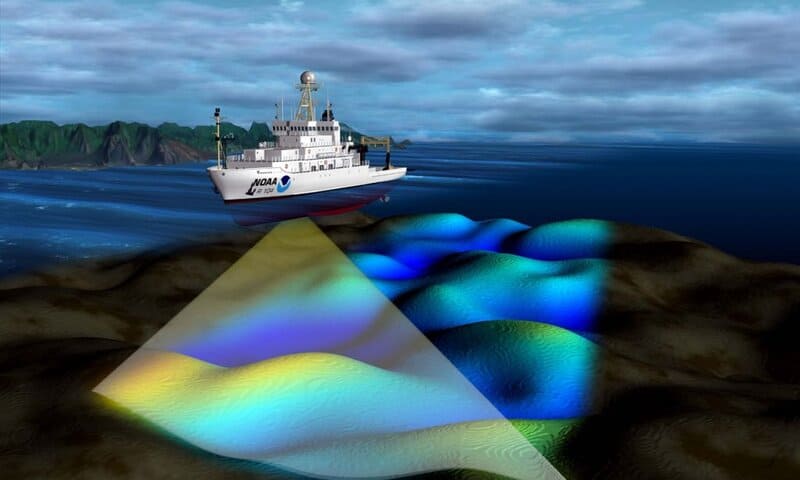

Cutting-edge technology is revolutionizing our understanding of the Arctic.
The U.S. Coast Guard icebreaker Healy uses multibeam echo sounders to generate detailed 3D maps of the ocean floor, exposing dramatic underwater features previously unseen.
One notable discovery is the Healy Seamount, a towering underwater mountain rising 3,000 meters from the seafloor.
These vivid 3D maps are more than scientific marvels—they are keys to unlocking the geological and biological mysteries of the deep Arctic.
Explore more at Ocean Today: Arctic Exploration.
4. Greenland’s Rare Earth and Critical Minerals

Greenland is quickly becoming a focal point for rare earth exploration, boasting substantial reserves of critical minerals essential for green technologies like wind turbines and electric vehicles.
As the Arctic ice recedes, new opportunities for mining are unveiled, drawing global attention to Greenland’s untapped potential.
This mineral wealth positions Greenland as a strategic hub in the world’s transition to renewable energy, sparking both excitement and debate over environmental and geopolitical impacts.
Discover more at Greenland’s Mineral Frontier.
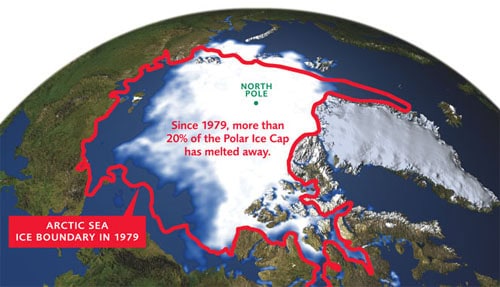
5. Accelerating Ice Melt Exposes Hidden Resources
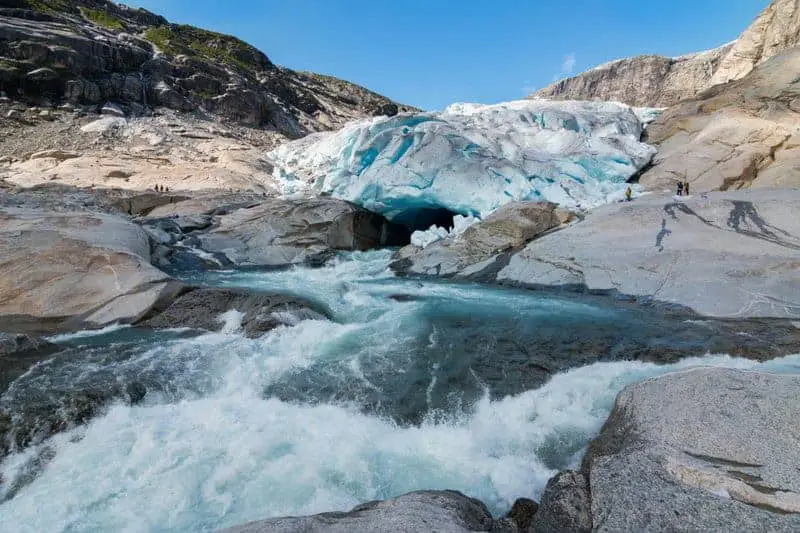

The Arctic is witnessing an unprecedented transformation, with ice melting at a staggering 30 million tonnes per hour.
This rapid loss uncovers vast swaths of land and seafloor once sealed off by ice, revealing untapped mineral and geological riches.
The dramatic shift is opening new frontiers for scientific research and resource extraction, fueling a race to understand and harness these newly accessible areas.
For further insight, visit Greenland’s Mineral Frontier.
6. Arctic Warming: Twice the Global Rate

The Arctic is heating up at nearly twice the pace of the rest of the planet, dramatically reshaping the region’s future.
This accelerated warming is opening up previously frozen sea routes and making resource-rich areas newly accessible.
As a result, nations are intensifying efforts to expand their territorial claims and strategic influence.
The climate-driven changes are not just environmental—they are actively redrawing the geopolitical boundaries of the Arctic.
Delve deeper at Geopolitics of the Arctic in 2025.
7. Opening of Arctic Shipping Routes

By 2025, the U.S. Navy projects that three major Arctic shipping routes will become navigable, thanks to extended open-water seasons.
These new corridors will dramatically reshape global trade by providing faster, more direct links between continents.
The opening of these routes is expected to boost economic activity in the region and heighten international interest and competition.
As shipping lanes evolve, the Arctic’s strategic importance will only grow.
Learn more at the U.S. Climate Resilience Toolkit.
8. Advanced Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs)
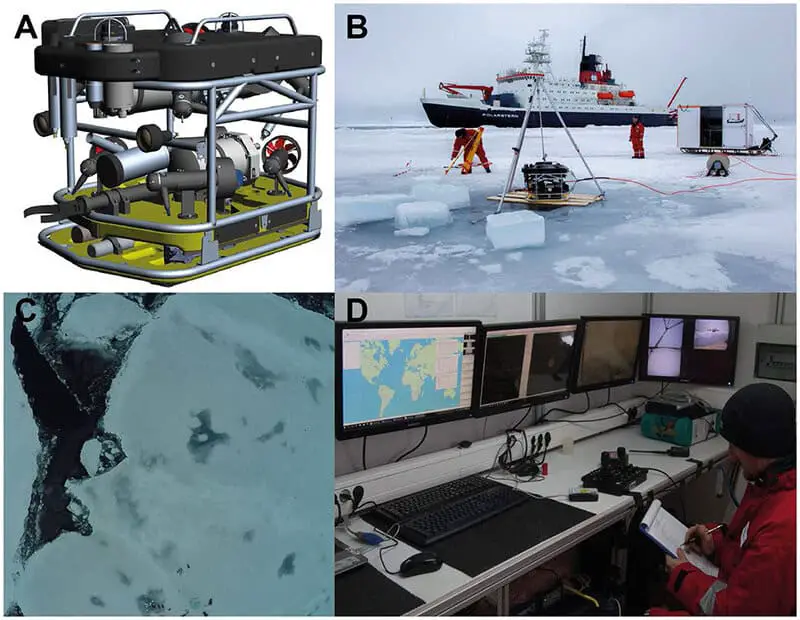

Cutting-edge Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) are transforming Arctic exploration.
Equipped with high-definition cameras and sophisticated sensors, these ROVs dive to astonishing depths—up to 9,000 feet—to capture footage of uncharted marine life and intricate seafloor landscapes.
Their precision and reach not only enable breathtaking scientific discoveries but also ensure safer, more efficient exploration in the region’s challenging conditions.
For a closer look at these remarkable tools, visit Ocean Today: Arctic Exploration.
9. Global Mineral Demand and Arctic Supply

The world’s appetite for minerals is projected to quadruple by 2040, driven by soaring demand for batteries, wind turbines, and electric vehicles.
Arctic resources—particularly Greenland’s rare earth elements—are poised to become crucial for powering the green transition.
As nations seek reliable sources for these strategic minerals, the Arctic’s importance as a global supplier is rapidly increasing.
This shift puts new economic and environmental pressures on the region.
Read more at Greenland’s Mineral Frontier.
10. Alaska’s Red Dog Mine: Zinc Powerhouse
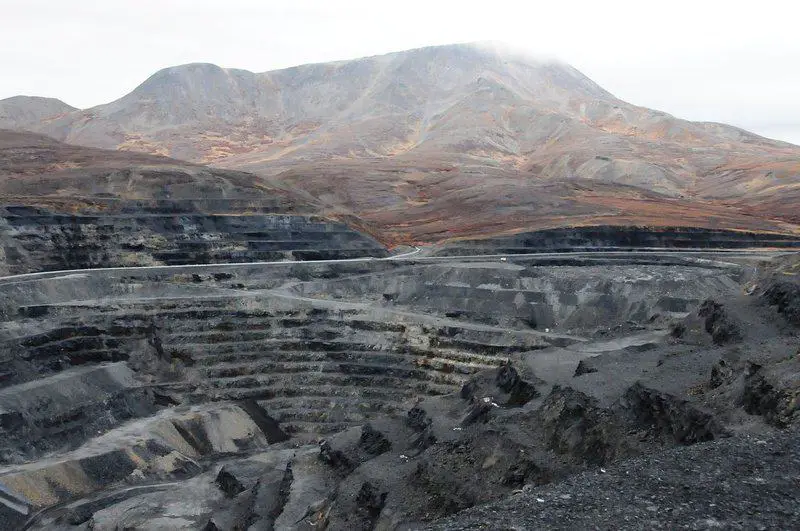

Alaska’s Red Dog Mine is a global powerhouse, holding nearly two-thirds of the United States’ zinc resources.
As one of the world’s top zinc producers, its ongoing expansion highlights both the vast mineral potential and the operational difficulties unique to the Arctic.
Red Dog stands as a testament to the region’s resource wealth and the logistical challenges inherent in remote, icy environments.
For more on Arctic mining, visit the U.S. Climate Resilience Toolkit.
11. Infrastructure Challenges: Ice Roads and Thawing Permafrost
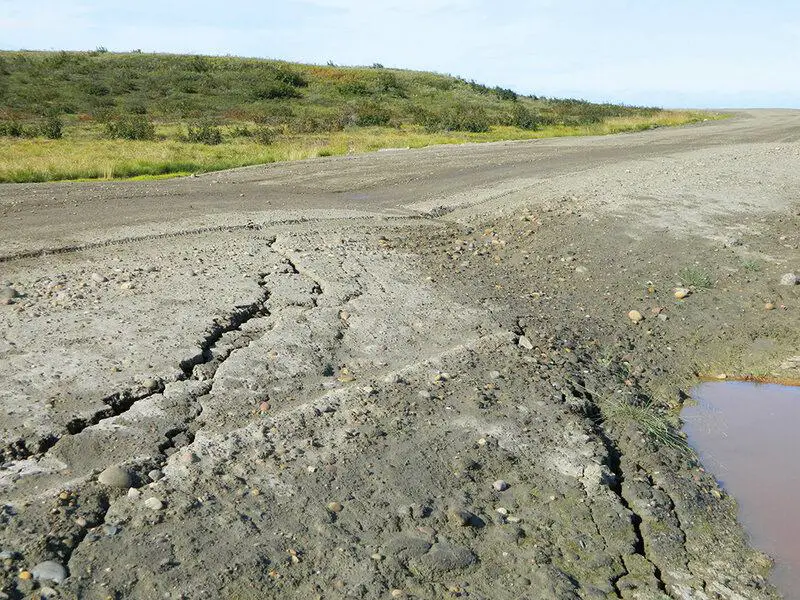

Building and maintaining infrastructure in the Arctic presents formidable challenges.
Ice roads only function seasonally, while thawing permafrost endangers buildings, pipelines, and vital supply routes.
These shifting conditions call for innovative engineering and adaptive logistics to ensure safe, sustainable development.
As the climate continues to change, overcoming these obstacles will become even more critical for future Arctic operations.
Explore solutions at the U.S. Climate Resilience Toolkit.
12. International Cooperation: The Arctic Council’s Role
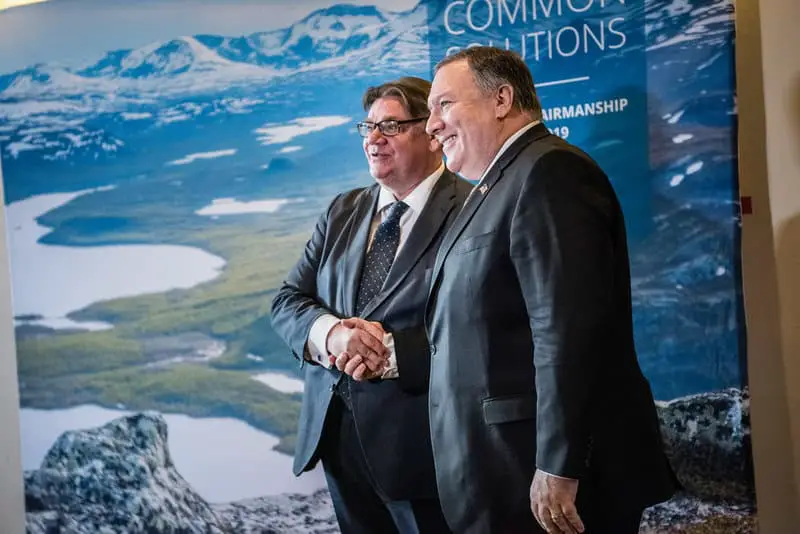

Effective stewardship of the Arctic depends on international collaboration.
Organizations like the Arctic Council play a central role in coordinating scientific research, managing territorial disputes, and safeguarding fragile ecosystems.
Their efforts foster dialogue and cooperation among Arctic nations, promoting sustainable development as the region undergoes dramatic transformation.
Such collaboration is essential for balancing resource extraction with environmental protection.
Learn more in the NOAA Arctic Vision and Strategy.
13. Territorial Claims and Geopolitical Tensions
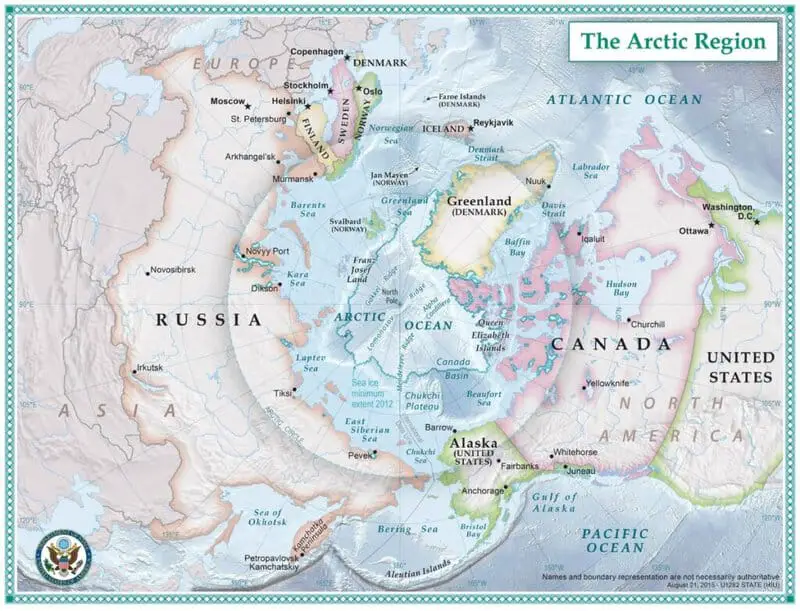
As the Arctic’s resources and shipping lanes become more accessible, major powers like the U.S., Russia, Canada, and Denmark are intensifying their efforts to stake territorial claims.
This competition heightens the risk of disputes over borders and resource rights, creating a complex web of geopolitical tensions.
Resolving these challenges peacefully is critical for regional stability.
For deeper analysis, see Geopolitics of the Arctic in 2025.
14. Oil and Gas Prospects Beneath the Ice
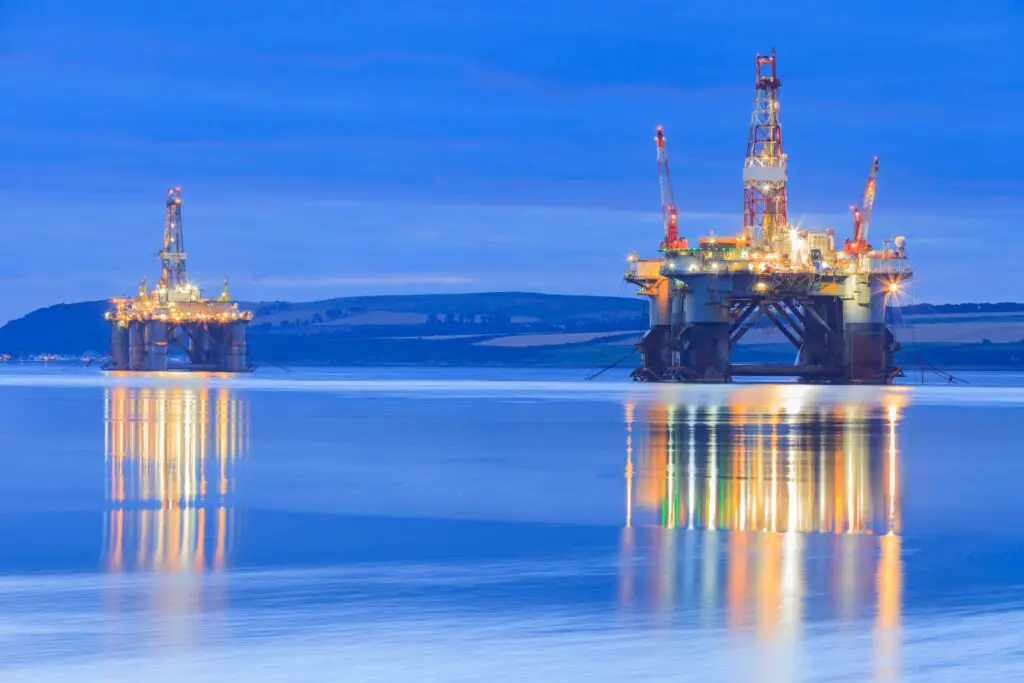

Beneath the Arctic’s icy surface lie immense energy reserves—an estimated 13% of the world’s undiscovered oil and 30% of its natural gas, primarily offshore.
As ice diminishes and extraction technology advances, these resources become increasingly accessible, holding the potential to reshape global energy markets.
This newfound availability fuels both opportunity and debate over environmental and geopolitical impacts.
For more details, visit U.S. Geological Survey Arctic Energy.
15. Indigenous Knowledge and Stewardship
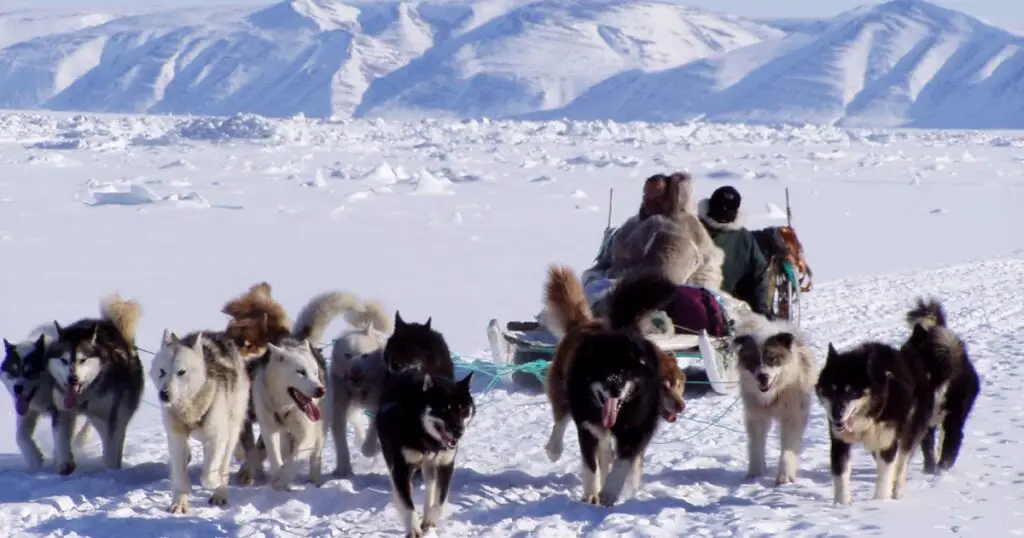

Indigenous communities have stewarded the Arctic for countless generations, holding deep, place-based knowledge of local ecosystems and sustainable resource management.
Their insights are invaluable for guiding responsible development and complementing scientific research efforts.
Collaboration with Indigenous peoples ensures that traditional wisdom shapes policy, conservation, and exploration in the rapidly changing region.
Recognizing and respecting this expertise is essential for a sustainable Arctic future.
Learn more at Arctic Council Indigenous Participation.
16. Arctic Biodiversity Hotspots
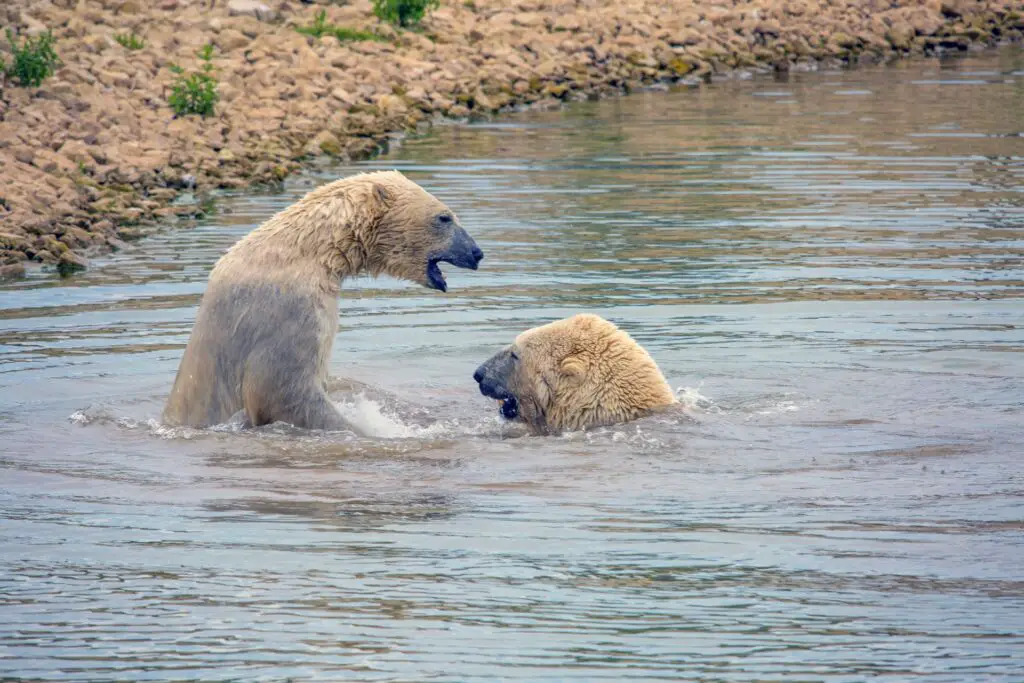

The Arctic supports a remarkable array of unique species—from elusive narwhals and iconic polar bears to vibrant deep-sea corals.
These biodiversity hotspots face mounting threats from climate change and increased human activity, including resource extraction.
Advanced mapping initiatives play a crucial role in identifying, monitoring, and protecting these fragile ecosystems.
Safeguarding Arctic biodiversity is essential for maintaining ecological balance in this rapidly changing region.
Explore more at NOAA Arctic Biodiversity.
17. Unexplored Underwater Mountains and Valleys

Recent 3D mapping efforts have uncovered a hidden world beneath the Arctic waves—unexplored underwater mountains, vast canyons, and hydrothermal vents.
These dramatic features provide vital clues about Earth’s geological history and create isolated habitats for remarkable, sometimes unknown, life forms.
Each new discovery challenges scientific assumptions and expands our understanding of the planet’s evolution.
For more on these wonders, visit Ocean Today: Arctic Exploration.
18. Carbon Sinks and Climate Feedback Loops

The Arctic’s extensive peatlands and deep seafloor sediments act as vital carbon sinks, locking away vast quantities of greenhouse gases.
However, as permafrost thaws, this stored carbon risks being released, potentially speeding up global warming and intensifying climate feedback loops.
Accurate mapping of these carbon reserves is essential for improving climate models and forecasting future changes.
Stay informed with the NOAA Arctic Report Card.
19. Fisheries and Food Security
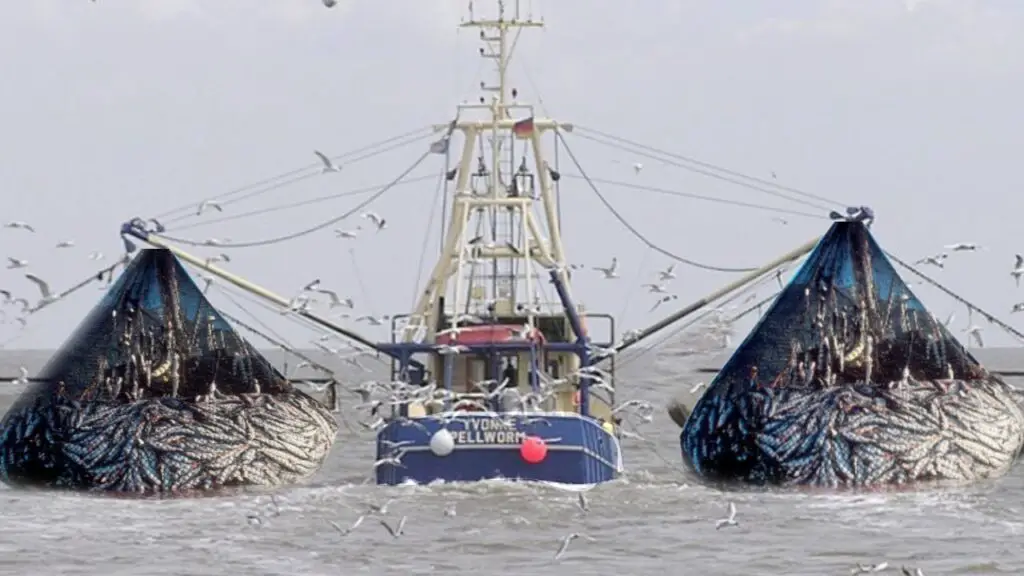

With the retreat of Arctic ice, fisheries are expanding into previously inaccessible waters.
This shift presents fresh opportunities for economic growth and food security, but also introduces new risks to ecosystem balance and local communities.
Comprehensive mapping and monitoring are essential for guiding sustainable fisheries management and safeguarding vital marine resources.
Responsible stewardship is key to ensuring both biodiversity and long-term livelihoods.
Find out more at NOAA Arctic Fisheries.
20. Microplastics and Pollution Monitoring

Recent mapping expeditions have uncovered the presence of microplastics and other pollutants even in the most remote Arctic waters.
This startling discovery highlights the far-reaching impact of global plastic circulation and underscores the vulnerability of the polar environment.
The findings call for robust, international collaboration to address pollution and safeguard Arctic ecosystems.
For more information, visit NOAA Arctic Pollution.
21. Under-Ice Ecosystems: A Hidden World

Beneath the Arctic sea ice lies a vibrant and mysterious world.
Advanced sensors have unveiled thriving ecosystems—ranging from microscopic algae to enigmatic invertebrates—uniquely adapted to the region’s harsh, frigid conditions.
Many of these under-ice species remain only partially understood, offering scientists fresh opportunities for discovery and insight into extreme life.
These hidden habitats are a reminder of how much is still left to uncover in the Arctic.
Learn more at Ocean Today: Arctic Exploration.
22. Permafrost Mapping and Methane Release
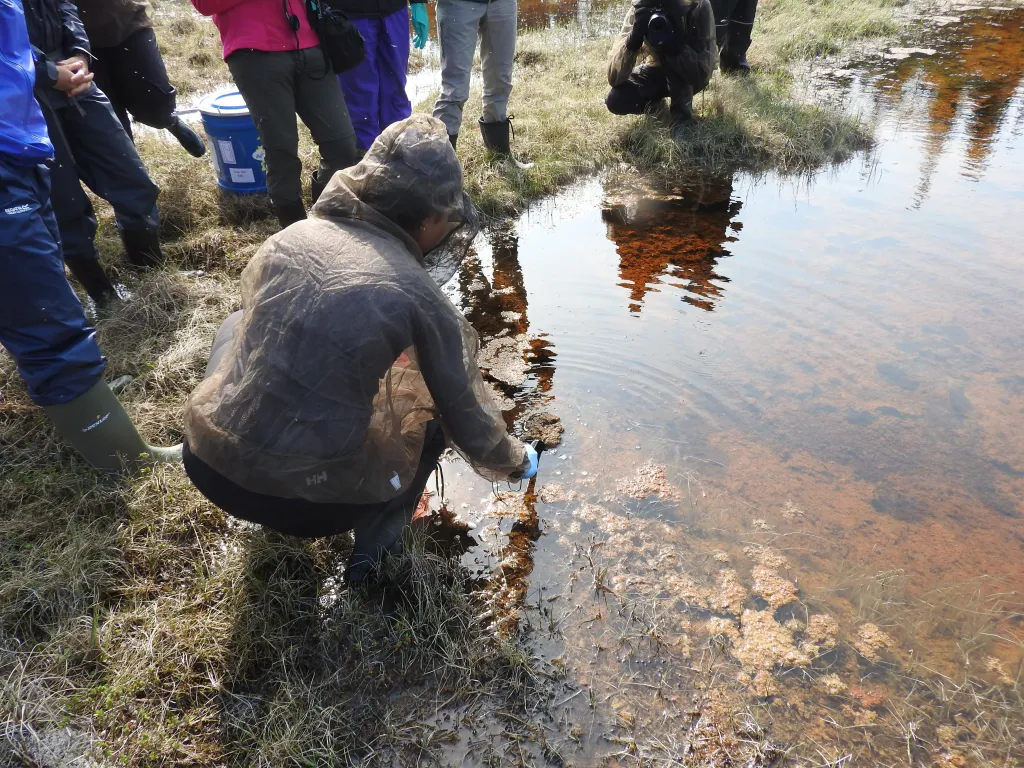

Advanced mapping of Arctic permafrost is crucial for tracking the release of methane, a highly potent greenhouse gas.
As Arctic soils thaw, detailed maps enable scientists to monitor vulnerable areas and provide vital early warnings of potential climate tipping points.
Understanding these dynamics is key to predicting global climate impacts and informing mitigation strategies.
Stay updated with the NOAA Arctic Report Card.
23. Satellite Remote Sensing: Eyes on the Arctic

Modern satellites armed with radar, lidar, and thermal sensors provide real-time insights into ice cover, shifting ocean currents, and landscape changes across the Arctic.
These advanced technologies have revolutionized how scientists monitor and understand the region’s rapid transformations.
Satellite data not only enhances research but also supports safer navigation and more effective resource management.
For the latest imagery and findings, explore NOAA Arctic Satellite Data.
24. The Race for Data: Open Science and Sharing
Open data initiatives are transforming Arctic exploration by making mapping results broadly available to researchers, policymakers, and the public.
This spirit of transparency accelerates scientific breakthroughs and supports global collaboration for sustainable development in the polar region.
By sharing knowledge and resources, the international community can address Arctic challenges more effectively and responsibly.
Access open Arctic data at NOAA Arctic Open Data.
25. The Future: Balancing Opportunity and Responsibility

The unfolding Arctic gold rush offers immense promise—precious minerals, new scientific frontiers, and transformative trade routes.
Yet, these opportunities come with a profound responsibility to protect fragile ecosystems and honor the rights and knowledge of indigenous peoples.
Sustainable exploration and careful stewardship will ultimately determine the legacy of this rapidly changing region.
The world faces a pivotal choice: pursue prosperity at the expense of the Arctic, or forge a future where opportunity and responsibility coexist.
Learn more in the NOAA Arctic Vision and Strategy.
Conclusion

The Arctic stands on the threshold of transformation, as pioneering mapping and exploration efforts uncover vast resources and scientific secrets.
This new era brings the promise of economic growth and discovery, yet demands vigilant stewardship to safeguard ecosystems and honor indigenous wisdom.
Balancing bold opportunity with responsible action is essential, for the Arctic remains one of Earth’s most mysterious and environmentally significant regions.
Its future will be shaped by the choices we make today—choices that echo across the globe and for generations to come.



Vielleicht interessiert es Sie:
13 Extraordinary Giants Ready to Blow Your Mind! 🌍
10 Chonky Oddities That Will Leave You Speechless! 🤯
9 Unbelievable Absolute Units That Will Leave You Speechless! 🌟
10 Colossal Creatures That Will Leave You Speechless! 🐻
12 Shocking Absolute Units You’ll Have to See! 😲
12 Epic Absolute Units That Will Challenge Your Perceptions! 🔥
Uncover the 11 Ultimate Massive Oddities That Awe! 🌍
9 Unbelievable Oddities That Redefine ‚Massive‘! 🐉💎