In recent years, Antarctica has transformed from a symbol of frozen desolation into a hotbed of scientific intrigue.
Armed with cutting-edge technology, researchers have pierced the continent’s thick icy shell,
revealing astonishing biological treasures where none were thought possible.
Beneath the relentless cold, vast subsurface rivers, ancient aquifers, volcanic caves,
and newly exposed seafloor ecosystems have come to light.
Each discovery peels back another layer of mystery, challenging our understanding of life’s resilience and adaptability.
With every expedition, scientists are rewriting the rules of biodiversity at the planet’s coldest frontier,
opening doors to a world teeming with organisms that defy expectation and redefine what it means to thrive in Earth’s harshest environment.
1. Subglacial Rivers: Life Flourishing in the Dark
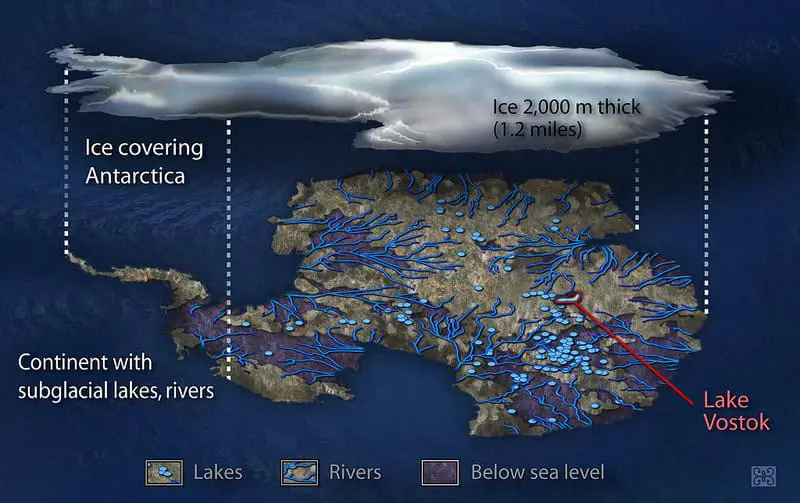
Hidden far below Antarctica’s ice, networks of subglacial rivers pulse with life in perpetual darkness.
In 2021, scientists discovered amphipods and other resilient organisms thriving over 1,600 feet beneath the Larsen Ice Shelf.
These creatures survive in frigid, isolated waters, adapting to extreme cold and scarce nutrients.
Such discoveries offer a rare window into how life endures in seemingly impossible conditions,
raising profound questions about the limits of survival on Earth—and perhaps beyond.
2. The 2025 Iceberg A-84 Breakaway: A Revealing Event
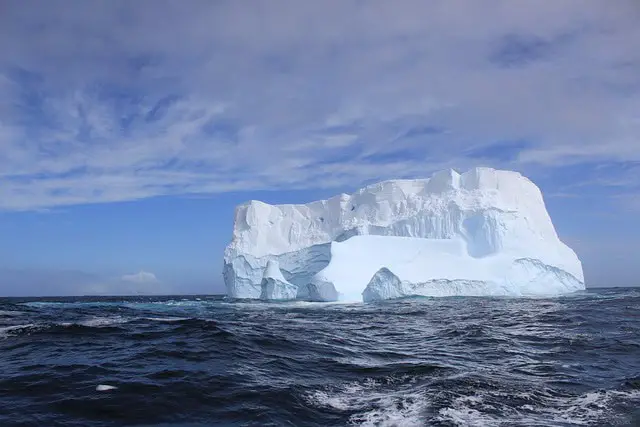

The dramatic calving of iceberg A-84 from the George VI Ice Shelf in January 2025 unveiled a hidden world below.
With the ice gone, researchers deployed remotely operated vehicles to explore the untouched seafloor, plunging to depths of 1,300 meters.
They discovered thriving communities—corals, sponges, icefish, and even giant sea spiders—adapted to the sudden change in environment.
These findings, detailed by the Schmidt Ocean Institute,
underscore the remarkable resilience and adaptability of Antarctic marine life.
3. Volcanic Caves: Cradles for Unique Life
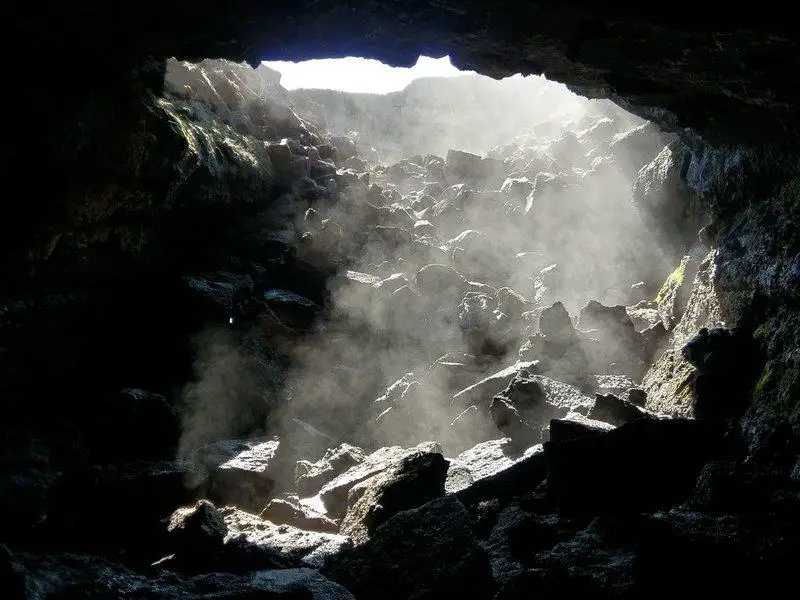

Beneath the icy slopes of Mount Erebus, scientists have uncovered intricate volcanic cave systems brimming with biological intrigue.
DNA traces from these caves suggest the presence of undiscovered species uniquely adapted to their warm, humid, and pitch-dark environment.
Researchers believe these subterranean sanctuaries may nurture complex microbial and fungal communities,
creating a hidden “new world” distinct from the harsh Antarctic surface.
For more on these findings, visit HowStuffWorks.
4. Remotely Operated Vehicles: Eyes in the Abyss
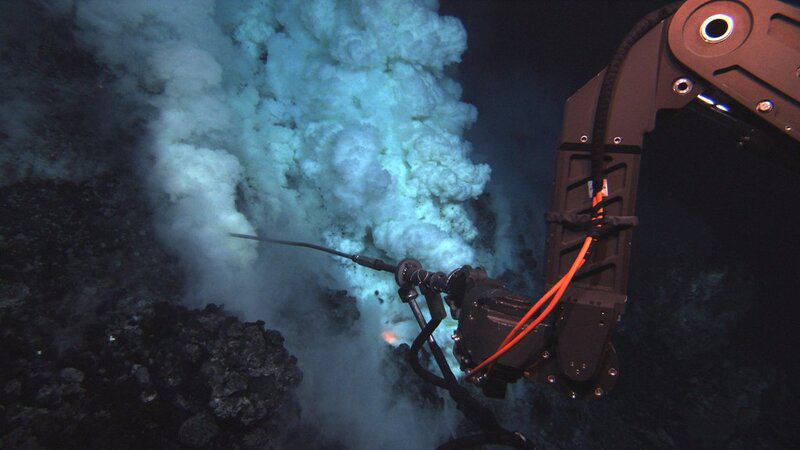

With the help of advanced remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), scientists have ventured as deep as 9,000 feet beneath the Antarctic ice.
Outfitted with high-definition cameras, these ROVs have revealed astonishing footage of unknown organisms and intricate ecosystems.
Each mission, such as those described by Live Science, is transforming our understanding of Antarctic biodiversity and the hidden depths of life.
5. Amphipods: Survivors of the Deep
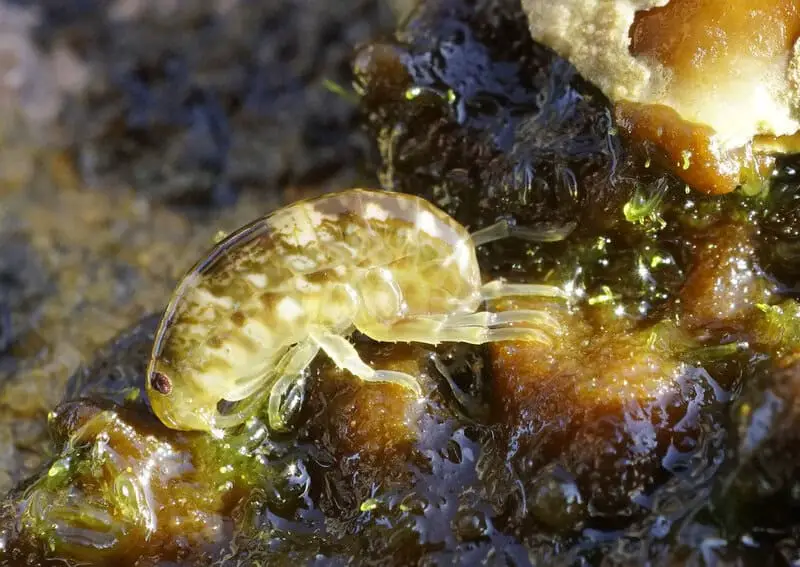

Amphipods, small yet resilient crustaceans, were among the first life forms found in Antarctic subglacial rivers.
Their remarkable ability to withstand extreme cold and perpetual darkness parallels adaptations seen in deep-sea vent species.
This striking similarity highlights a case of convergent evolution, as detailed by
National Geographic.
6. Giant Sea Spiders: Antarctic Titans
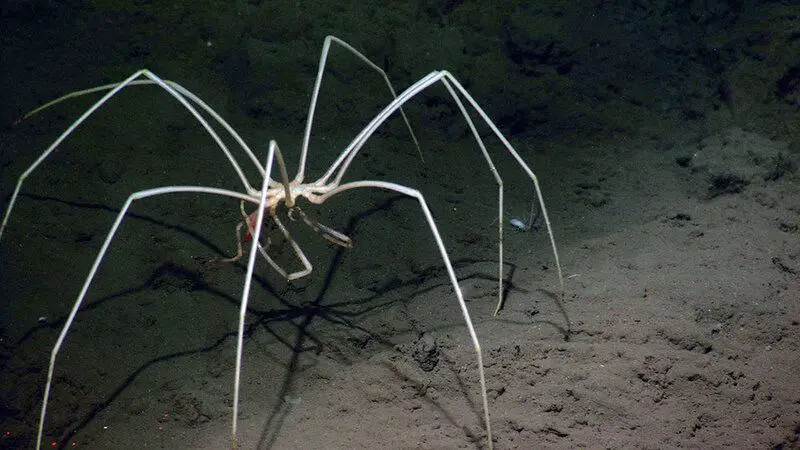

Beneath the ice, giant Antarctic sea spiders—some as large as dinner plates—have been discovered thriving in the frigid, oxygen-rich waters exposed by recent iceberg calving.
These remarkable creatures exemplify polar gigantism, where low temperatures and high oxygen availability fuel extraordinary growth.
For more on these Antarctic titans, see Scientific American.
7. Icefish: Masters of Antifreeze

Antarctic icefish are extraordinary for their ability to survive in subzero waters, thanks to special antifreeze proteins in their blood.
These unique adaptations prevent ice crystals from forming, enabling the fish to thrive where few others can.
Researchers see icefish as vital models for understanding how animals colonize extreme environments (BBC News).
8. Ancient Seawater Aquifers
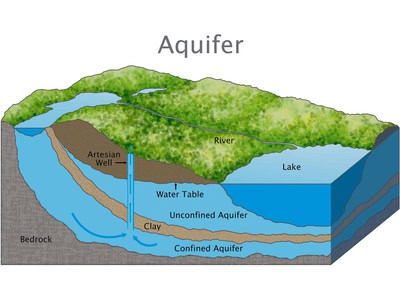
Using lidar and magnetotelluric imaging, researchers have identified vast aquifers of ancient seawater buried beneath West Antarctica’s ice streams.
These hidden reservoirs may harbor unique microbial ecosystems, isolated for millennia from the outside world.
Additionally, the presence of these aquifers could significantly influence ice sheet stability and Antarctic hydrology.
For further exploration, see Smithsonian Magazine.
9. Corals and Sponges: Deep Sea Builders
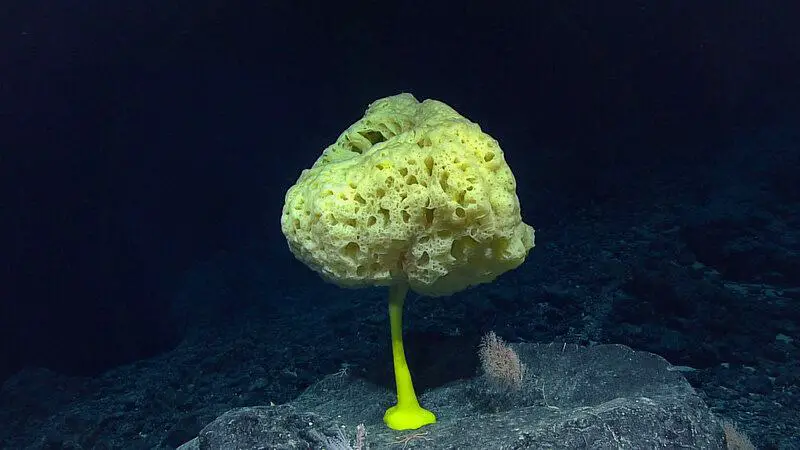

Beneath the Antarctic ice, scientists have discovered complex coral and sponge communities thriving in the dark.
These organisms serve as ecosystem architects, filtering nutrients from the water and providing essential habitat for a variety of other species.
Their presence highlights the rich biodiversity hidden below the surface (Schmidt Ocean Institute).
10. Octopuses: Surprising Residents
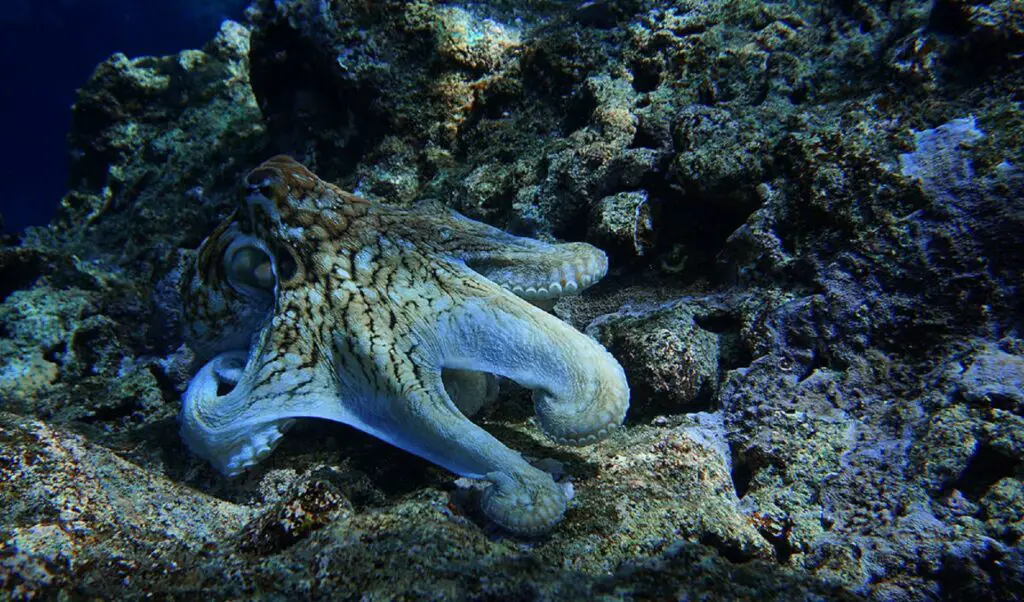

Beneath Antarctica’s ice, researchers have found octopuses with remarkable adaptations for extreme cold.
These cephalopods utilize specialized hemocyanin to efficiently transport oxygen in frigid waters, echoing the survival tactics of their deep-sea relatives.
Their unique biology further expands our understanding of life’s adaptability (Euronews).
11. Microbial Mats: Ancient Survivors

In the darkness of subglacial lakes, microbial mats thrive by tapping into chemical energy rather than sunlight.
These ancient communities offer a glimpse into how life might have existed on early Earth—and even on other planets.
Their resilience and metabolic ingenuity are detailed in Nature, highlighting the remarkable adaptability of Antarctic microbes.
12. DNA Evidence of New Species
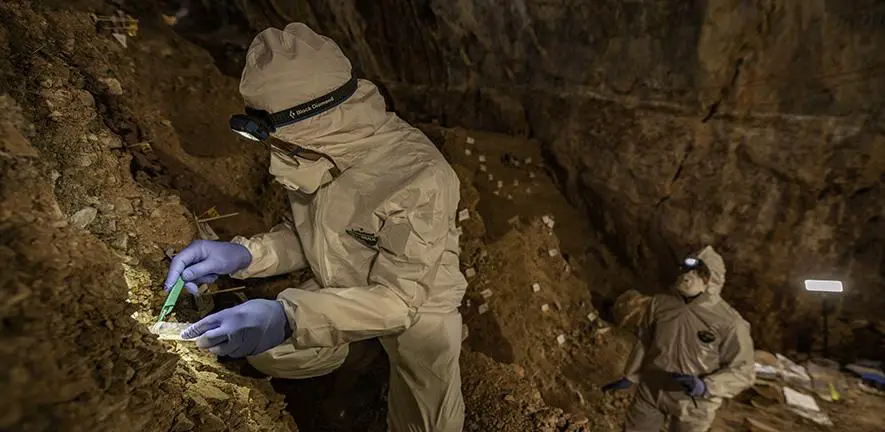

Recent studies of environmental DNA (eDNA) collected from volcanic caves and sub-ice environments have revealed genetic signatures of numerous, yet-undescribed species.
Ongoing genetic analyses indicate high levels of endemism, with many organisms likely unique to Antarctica’s hidden habitats.
These findings, highlighted in Newsweek, underscore the extraordinary biodiversity that remains to be formally identified and cataloged beneath the ice.
13. Ice Shelf Breakaways: Nature’s Laboratory
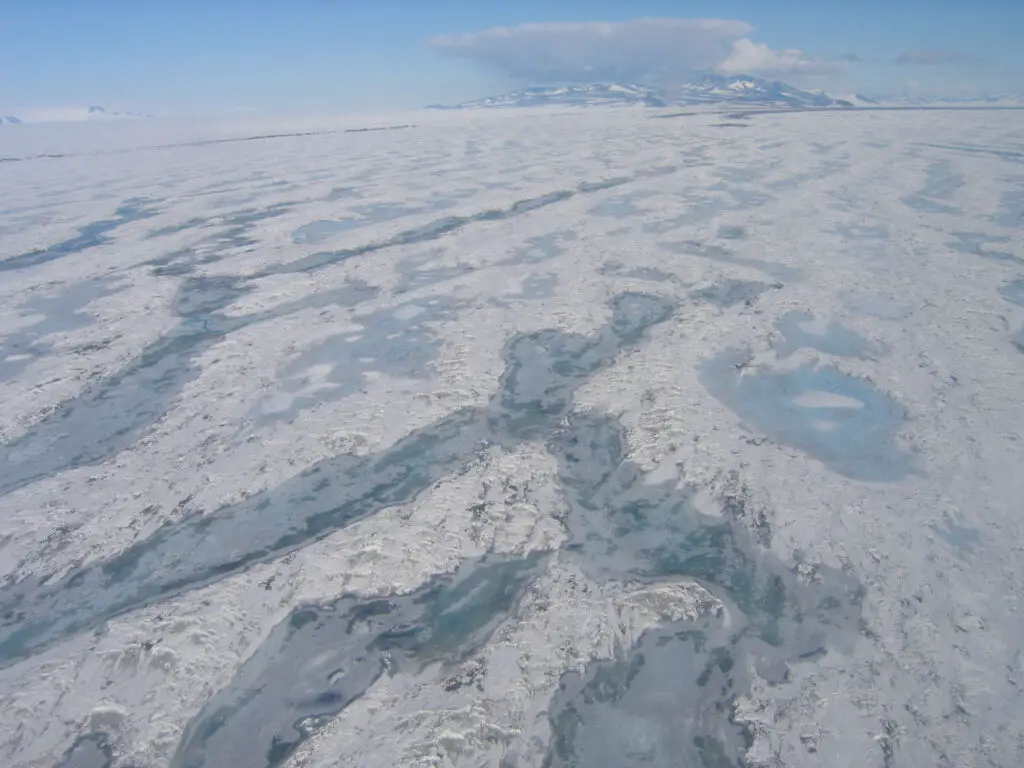

The dramatic calving of ice shelves, such as the A-84 event, creates rare windows into untouched Antarctic ecosystems.
These sudden exposures allow scientists to observe how life rapidly adapts to new, challenging conditions.
Such natural laboratories are invaluable for studying ecological resilience and change (Schmidt Ocean Institute).
14. Hidden World Beneath the Ice

Scientists were astounded to find a vast ‘hidden world’ beneath the Antarctic ice, unveiled through stunning high-definition footage.
Dense communities of filter feeders and predators flourished in these concealed habitats, showcasing unexpected biodiversity.
This discovery, detailed by Live Science, has redefined what we thought possible under the frozen surface.
15. Endurance in Isolation

Antarctica’s hidden ecosystems have survived centuries of isolation from surface nutrients, evolving extraordinary resilience.
Much like species on remote islands, these organisms have adapted to thrive in resource-scarce, extreme conditions.
Their endurance highlights the relentless creativity of life in the face of adversity (Euronews).
16. Lidar and Magnetotelluric Imaging: Mapping the Unknown
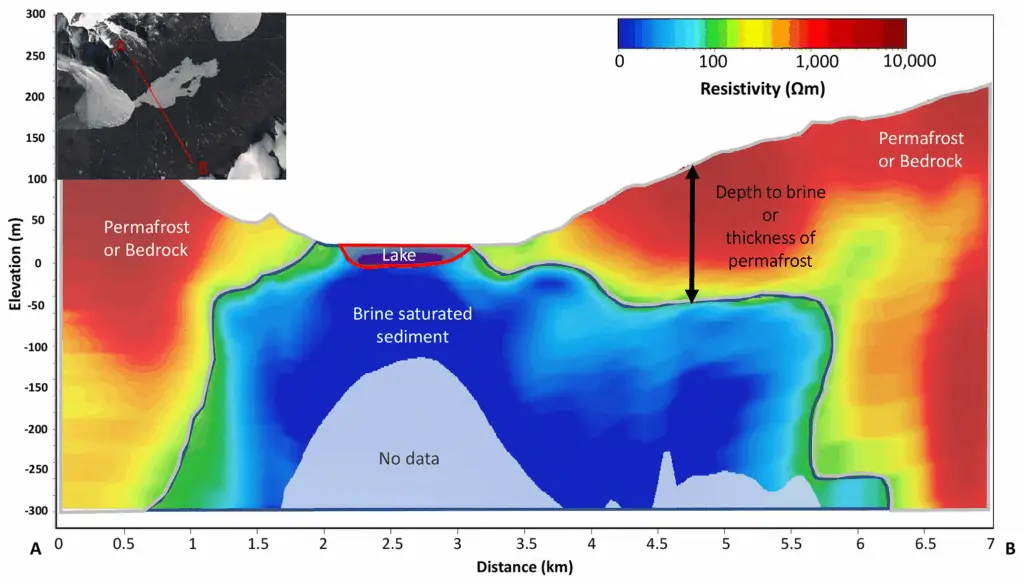
Cutting-edge lidar and magnetotelluric imaging are transforming our ability to map Antarctica’s subsurface landscapes.
These advanced tools reveal the vast networks of underground water, caves, and hidden habitats that were once inaccessible.
Their use is rapidly expanding our knowledge of the continent’s secret ecosystems (Smithsonian Magazine).
17. Intricate Ice Caves: Biodiversity Hotspots
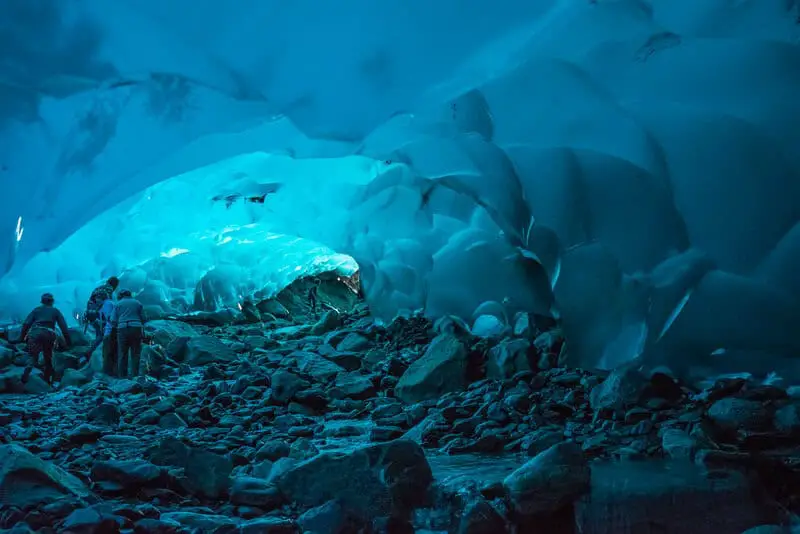

Antarctica’s intricate ice caves are emerging as unexpected biodiversity hotspots.
Researchers suspect these caves could shelter complex plant and animal communities, potentially rivaling the diversity found in temperate cave systems.
Each new discovery within these frozen labyrinths reshapes our view of Antarctic life (HowStuffWorks).
18. Chemosynthetic Life: Energy Without Sunlight

Beneath Antarctic ice, many organisms survive by chemosynthesis—deriving energy from chemical reactions rather than sunlight.
This strategy mirrors the life found at deep-sea hydrothermal vents, enabling communities to thrive in perpetual darkness.
Such adaptations broaden our understanding of where and how life can exist (Nature).
19. Potential for New Medicines

Antarctica’s unique microbes and invertebrates produce enzymes and compounds unlike any found elsewhere.
These biochemical treasures could pave the way for innovative new medicines, much like breakthroughs from other extreme environments.
Ongoing research is already yielding promising leads for future drug development (NIH).
20. Challenging the Limits of Life

The astonishing discoveries under Antarctica’s ice are compelling scientists to rethink the boundaries of life’s resilience.
These findings parallel revelations from the deep sea and even insights gained from space exploration.
Antarctica’s hidden ecosystems challenge our understanding of biology and hint at possibilities beyond our planet (Newsweek).
21. Implications for Climate Change and Conservation

Studying the resilience and adaptability of Antarctica’s hidden life is essential for anticipating how ecosystems worldwide may respond to climate change.
These discoveries inform global conservation efforts, highlighting the urgent need to protect vulnerable polar habitats.
By unraveling the secrets of these unique communities, scientists can better guide strategies to preserve Earth’s most extraordinary environments (Scientific American).
22. Future Exploration: The Next Frontier

Antarctica remains a realm of tantalizing mystery, with vast unexplored regions beneath its ice.
Rapid advances in technology promise to unlock even deeper secrets, allowing researchers to probe further into this alien environment.
The next wave of exploration could reveal entirely new forms of life, forever expanding our understanding of biology (Nature).
23. Years of Analysis Ahead

Despite the excitement around newly discovered organisms, confirming new species in Antarctica is a painstaking process.
Researchers face years of meticulous genetic and morphological analysis before these life forms can be formally described.
This slow but essential work will shape our understanding of Antarctic biodiversity for generations (Scientific American).
Conclusion

The flood of revolutionary discoveries beneath Antarctica’s ice is rewriting the boundaries of biology and inspiring awe at life’s tenacity.
From subglacial rivers and volcanic caves to ancient aquifers and hidden seafloor communities, these ecosystems reveal how life persists against all odds.
They challenge our assumptions, offering vital clues about Earth’s evolutionary history and its uncertain future.
As technology enables deeper exploration, it is crucial to support and protect these fragile environments—not just as scientific frontiers, but as extraordinary testaments to life’s adaptability.
Let these revelations fuel our curiosity, stewardship, and respect for our planet’s most mysterious habitats.



Vielleicht interessiert es Sie:
13 Extraordinary Giants Ready to Blow Your Mind! 🌍
10 Chonky Oddities That Will Leave You Speechless! 🤯
9 Unbelievable Absolute Units That Will Leave You Speechless! 🌟
10 Colossal Creatures That Will Leave You Speechless! 🐻
12 Shocking Absolute Units You’ll Have to See! 😲
12 Epic Absolute Units That Will Challenge Your Perceptions! 🔥
Uncover the 11 Ultimate Massive Oddities That Awe! 🌍
9 Unbelievable Oddities That Redefine ‚Massive‘! 🐉💎