Imagine a world where time itself can slow down or speed up depending on how fast you move.
This isn’t science fiction—it’s a reality for astronauts racing through space.
Thanks to Einstein’s theory of relativity,
we now know that time and speed are deeply connected.
When astronauts travel at incredible velocities, their experience of time actually diverges from ours on Earth.
This remarkable truth means that every astronaut who ventures into orbit becomes, in a sense, a real-life time traveler—ushering in profound implications for science, technology, and even human identity.
1. The Science of Time Dilation
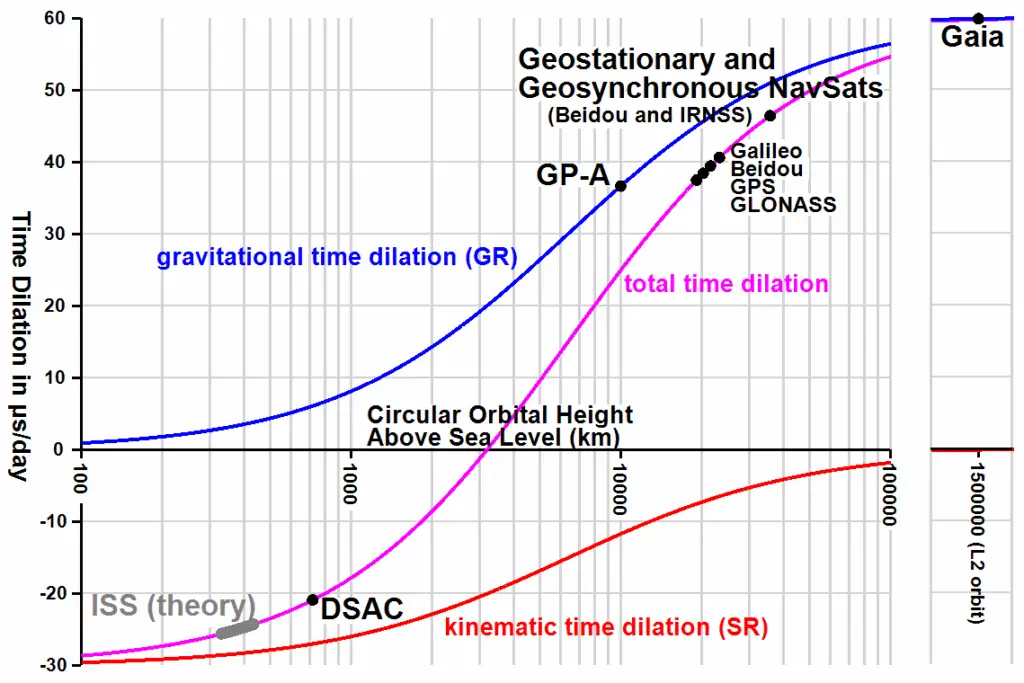
At the heart of relativity lies a mind-bending idea: time isn’t absolute.
According to Einstein, the faster an object moves, the slower time ticks for it compared to a stationary observer.
This phenomenon, called time dilation, has been confirmed through countless experiments and is especially noticeable at speeds approaching light.
For astronauts hurtling through space, this means their onboard clocks run just a bit slower than those on Earth.
Learn more at NASA.
2. The Twins Paradox

A classic way to picture time dilation is the Twins Paradox.
Imagine identical twins: one stays on Earth while the other blasts off into space at near-light speed.
When the traveler returns, they’re physically younger than their Earth-bound sibling.
This isn’t just a quirky idea—it’s a real consequence of relativity, vividly demonstrating how space travel can shift the flow of time.
Read more at Scientific American.
3. Real-Life Astronaut Examples

Time travel isn’t just theoretical—it’s been measured in real astronauts.
Take Scott Kelly, who spent 340 days aboard the International Space Station.
While his brother Mark stayed on Earth, Scott’s high-speed orbit meant he aged slightly less—by a fraction of a second.
This tiny difference, though minuscule, is direct evidence of time dilation at work, showing how every astronaut becomes a time traveler with each mission.
4. The International Space Station’s Speed

Orbiting Earth at an astonishing 28,000 km/h, the International Space Station (ISS) is a real-world laboratory for time dilation.
Astronauts aboard the ISS experience time just a little more slowly than we do on the ground.
Over the course of long missions, this difference adds up to mere milliseconds—but it’s a measurable effect!
Learn more at ESA.
5. Time Difference: The Numbers

The effect of time dilation may sound subtle, but it’s real and measurable.
During a six-month stint on the ISS, an astronaut will age about 0.007 seconds less than someone on Earth.
While this isn’t enough to notice in daily life, it’s a remarkable testament to relativity in action.
See the details at Live Science.
6. Traveling Closer to Light Speed

If we could send astronauts in spacecraft traveling near the speed of light, the effects of time dilation would become extraordinary.
Time for these travelers would slow down dramatically compared to people on Earth.
In theory, an astronaut could journey across the stars for just a few years—only to return and find that decades or even centuries had passed on Earth.
Read more at Physics World.
7. GPS Satellites and Time Correction
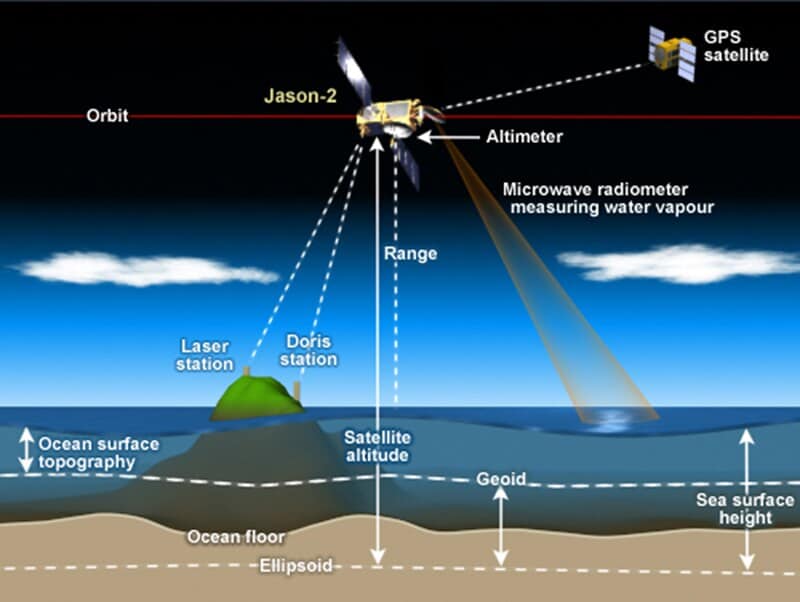
Time dilation isn’t just for astronauts—it affects the technology we rely on every day.
GPS satellites orbit Earth at high speeds and experience weaker gravity, which causes their clocks to tick differently than those on the ground.
Without constant adjustments, GPS calculations would quickly become inaccurate.
This real-world challenge is solved by applying Einstein’s relativity, keeping navigation systems precise.
Learn more at NASA Space Place.
8. Gravity’s Role: General Relativity

Gravity isn’t just about keeping our feet on the ground—it also shapes how we experience time.
According to general relativity, the stronger the gravitational pull, the slower time passes.
That means astronauts in orbit, farther from Earth’s mass, actually age slightly faster than those on the surface.
This fascinating effect is another way space travel subtly transforms astronauts into time travelers.
Learn more at Stanford.
9. Time Travel in Sci-Fi vs. Reality

Unlike the wild time jumps of science fiction, real-life time travel is subtle—measured in milliseconds, not centuries.
Astronauts don’t hop between eras, but their journeys prove that time can shift in measurable ways.
Reality grounds the fantasy: the small changes astronauts experience reinforce that time travel, though less dramatic, is undeniably real.
Source: Smithsonian Magazine.
10. Why We Don’t Notice the Change

Even though astronauts are technically time travelers, the effects are so slight—just fractions of a second—that they’re impossible to sense.
No astronaut feels younger or out of sync upon returning to Earth.
These changes are only detectable with incredibly precise instruments.
It’s a mind-bending idea, but one that plays out quietly, hidden in scientific data.
Reference: BBC.
11. Aging Backwards? The Myth Debunked

Despite some pop culture exaggerations, astronauts don’t actually age backwards or grow younger in space.
They simply age a tiny bit slower compared to people on Earth.
The difference is subtle, not a reversal of time’s arrow.
More from NASA.
12. The Future of Human Space Travel

As humanity sets its sights on Mars and deep space, time dilation will become even more noticeable.
Future astronauts on long-duration missions will experience greater differences in time compared to their loved ones on Earth.
The farther and faster we travel, the more pronounced this effect becomes—turning explorers into ever more remarkable time travelers.
Read more at Space.com.
13. The Hafele-Keating Experiment

In 1971, physicists Hafele and Keating tested Einstein’s predictions by flying atomic clocks around the world on commercial airplanes.
When compared with clocks left on the ground, the airborne clocks showed measurable time differences—just as relativity predicted.
This groundbreaking experiment provided concrete, real-world evidence that motion and gravity can truly alter the passage of time.
Details on Wikipedia.
14. The Role of Atomic Clocks

Atomic clocks are at the heart of measuring time dilation.
These ultra-precise instruments can detect even the tiniest differences in the passage of time—differences that would be invisible otherwise.
From space missions to satellite navigation, atomic clocks make it possible to observe and confirm relativity’s predictions with extraordinary accuracy.
Source: NIST.
15. Deep Space Probes and Time
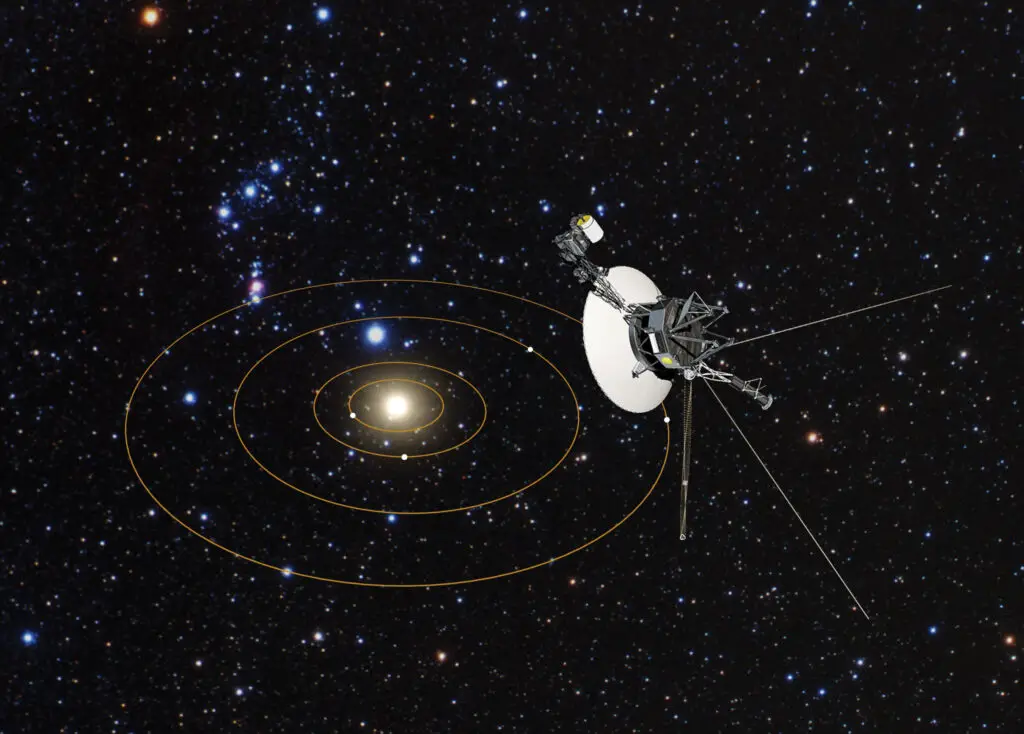
Even robotic explorers like the Voyager probes experience time differently as they speed through deep space.
While these effects are far less pronounced than with near-light-speed travel, they’re still present—and measurable.
It’s another reminder that every object in motion is subject to the strange flow of time predicted by relativity.
Learn more at JPL.
16. Space Tourism and Time Travel

With commercial space tourism on the rise, more ordinary people will soon experience time dilation firsthand—even if only by a few microseconds.
These tiny shifts will make the reality of time travel a shared experience, transforming a once far-off scientific concept into something personal and relatable.
Source: Space.com.
17. Comparing Astronauts and Airline Pilots

It’s not just astronauts who experience the effects of time dilation—airline pilots do, too, though on a much smaller scale.
Commercial pilots who log thousands of flight hours age ever-so-slightly less than those on the ground, due to both their speed and altitude.
However, the difference is even tinier than what astronauts face.
More at Wired.
18. Black Holes and Extreme Time Travel

If astronauts ventured close to a black hole, they’d encounter the most dramatic form of time dilation imaginable.
Near a black hole’s event horizon, gravity is so intense that time can slow to a near standstill compared to distant observers.
While this scenario is far beyond current spaceflight, it’s rooted in the same principles that govern astronaut time travel—just taken to cosmic extremes.
Read more at NASA.
19. Time as a Fourth Dimension

In Einstein’s universe, time is more than just a ticking clock—it’s a fourth dimension woven into the very fabric of reality.
Speed and gravity can stretch or compress this dimension, letting astronauts and probes chart new courses through spacetime.
Every journey off Earth is a step into this fourth dimension, making space travelers pioneers in ways we’re only beginning to understand.
Learn more at Britannica.
20. Philosophical Implications

The fact that astronauts are genuine time travelers forces us to rethink what time really means.
Their experiences blur the line between past, present, and future, stirring up profound questions about existence and our place in the cosmos.
Are we simply moving through a fixed spacetime, or is our journey more dynamic than we imagine?
Explore the philosophy at Aeon.
21. The Ultimate Time Machines: Future Technology

Looking ahead, advanced propulsion systems—like nuclear or antimatter drives—could one day propel spacecraft much closer to light speed.
Such breakthroughs would amplify the effects of time dilation dramatically, letting future explorers experience years while centuries pass on Earth.
These “ultimate time machines” are still theoretical, but they push the boundaries of what’s possible for human time travel.
More at Scientific American.
22. How Scientists Measure Time in Space
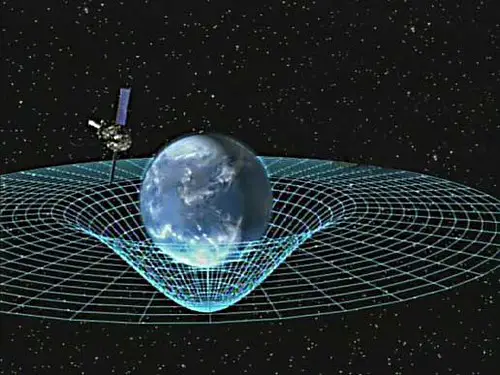
Scientists rely on atomic clocks and sophisticated timing signals to track even the tiniest differences in time experienced by astronauts and satellites.
By syncing clocks between Earth and space and comparing results, they can observe relativity in action with stunning precision.
These measurements are key to understanding—and verifying—the time travel of spacefarers.
Source: NIST.
23. The Psychological Impact

The realization that you’re a time traveler—even by mere milliseconds—can spark deep reflection in astronauts.
Some may feel a unique sense of separation or connection to loved ones, knowing their time is ever so slightly out of sync.
This subtle shift adds a psychological layer to the already profound experience of space travel.
Learn more at Psychology Today.
24. Time Travel on Return to Earth

When astronauts come home, they’ve effectively leaped a fraction of a second into Earth’s future.
Compared to friends and family, their clocks are minutely behind, making them genuine—if subtle—time travelers.
This phenomenon highlights the remarkable relationship between motion, gravity, and the flow of time for those who venture beyond our planet.
Source: NASA.
25. Our Everyday Time Travelers

Every astronaut who leaves Earth becomes an everyday time traveler, living proof of the universe’s strange and beautiful laws.
Their journeys remind us that even brief ventures into space connect us to the deepest mysteries of existence, blurring the boundaries between science fiction and reality.
More at Space.com.
Conclusion

The reality that space travel transforms astronauts into time travelers is more than a scientific curiosity—it’s a profound reminder of our universe’s complexity.
From fractional seconds lost or gained on each mission to the grand possibilities of future exploration, time dilation reshapes our understanding of existence, technology, and destiny.
As we reach for the stars, let’s marvel at how each journey not only unlocks new frontiers in science, but also brings us closer to the mysteries of time itself.



Vielleicht interessiert es Sie:
13 Extraordinary Giants Ready to Blow Your Mind! 🌍
10 Chonky Oddities That Will Leave You Speechless! 🤯
9 Unbelievable Absolute Units That Will Leave You Speechless! 🌟
10 Colossal Creatures That Will Leave You Speechless! 🐻
12 Shocking Absolute Units You’ll Have to See! 😲
12 Epic Absolute Units That Will Challenge Your Perceptions! 🔥
Uncover the 11 Ultimate Massive Oddities That Awe! 🌍
9 Unbelievable Oddities That Redefine ‚Massive‘! 🐉💎