In a stunning revelation, marine biologists have uncovered a 60,000-year-old underwater forest hidden beneath the waves off Alabama’s Gulf Coast.
This ancient cypress woodland, perfectly preserved in the ocean’s depths, offers a rare window into Earth’s distant past.
The incredible find has captivated both the scientific community and the public, raising tantalizing questions about prehistoric ecosystems, ancient climate, and the forces that shaped our planet.
As researchers dive into this submerged time capsule, the world awaits answers that could redefine our understanding of history and the resilience of nature.
1. The Discovery: A Hidden Forest Revealed

The ancient forest’s story began in 2004, when Hurricane Ivan churned up the Gulf of Mexico and violently shifted the seafloor.
This powerful storm stripped away layers of sediment, unexpectedly exposing cypress tree stumps and logs long buried beneath the ocean.
Local divers exploring the area stumbled upon the mysterious, woody remains and soon alerted marine scientists.
Their findings sparked a surge of interest, prompting research teams to investigate this extraordinary submerged landscape now visible for the first time in millennia.
2. Who Found the Forest?

The initial discovery by divers soon drew the attention of marine biologists from the University of Southern Mississippi and several collaborating institutions.
These expert researchers quickly organized expeditions to document and study the forest.
Their collaborative efforts combined advanced technology with scientific curiosity, turning a chance encounter by local adventurers into a groundbreaking research opportunity that continues to fascinate the scientific community and beyond.
3. Where Is It Located?
The ancient forest lies approximately 60 feet beneath the surface of the Gulf of Mexico, about 10 miles south of Mobile, Alabama.
This remarkable site is hidden beneath murky waters, nestled on the ocean floor where few would suspect such a prehistoric treasure awaits.
Its secluded location has helped preserve the forest’s unique features for tens of thousands of years.
4. How Old Is the Forest?
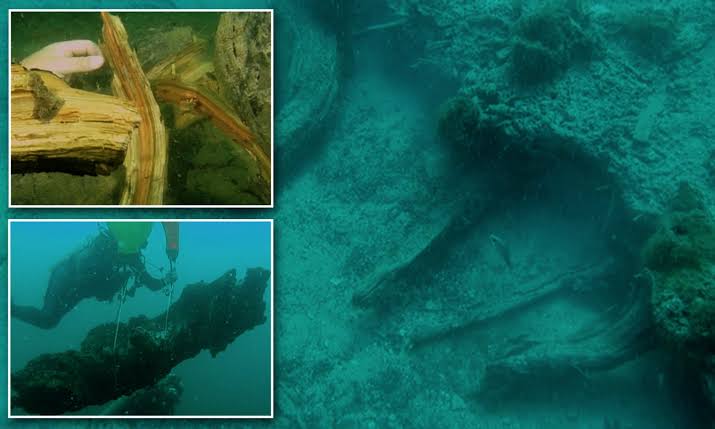

Radiocarbon dating performed on the preserved cypress wood revealed the forest’s astonishing age—approximately 60,000 years old.
This places its origin firmly in the last ice age, a period when sea levels were dramatically lower and the land now underwater was dry and teeming with life.
Such ancient preservation offers a valuable glimpse into a world long vanished.
5. What Type of Trees Were Found?

The underwater forest is dominated by the remains of ancient cypress trees, their trunks and stumps astonishingly well-preserved beneath layers of sediment.
Cypress wood is naturally resistant to rot, and the oxygen-starved environment under the seafloor further protected these relics from decay.
Researchers have been able to examine intact bark, tree rings, and even roots, offering rare insights into prehistoric plant life.
6. Sediment Burial: Nature’s Time Capsule

Over thousands of years, thick layers of sediment gradually buried the ancient forest, effectively sealing it off from oxygen and decay.
This natural process acted as a protective barrier, preserving the wood in remarkable condition.
The sediment served as a time capsule, allowing scientists to study these prehistoric trees and uncover secrets from an era long before modern civilization.
7. The Ice Age Connection

The forest dates back to the last glacial maximum, a period when massive ice sheets covered much of the Northern Hemisphere and global sea levels were far lower than today.
Back then, the area now submerged was dry land, teeming with cypress groves and wildlife.
As the ice age ended and glaciers melted, rising seas inundated the forest, preserving it under layers of sediment for millennia.
8. Pre-Ice Age Climate Insights

By analyzing growth rings and wood samples from the underwater cypress trees, scientists can reconstruct ancient climate patterns and environmental conditions.
These findings reveal details about precipitation, temperature, and even wildfire frequency thousands of years ago.
Such insights help researchers better understand how ecosystems responded to past climate shifts, offering valuable context for predicting the impacts of current and future environmental changes.
9. Biodiversity: A Refuge for Marine Life

The sunken cypress forest has become an oasis of biodiversity beneath the Gulf’s surface.
Its intricate root systems and fallen logs provide shelter, breeding grounds, and food for a variety of marine creatures—from fish and crabs to sea anemones and sponges.
This unexpected habitat supports a thriving community, demonstrating how ancient landscapes can continue to shape modern ecosystems in remarkable ways.
10. Rare Fungi and Bacteria Discovered
Scientists exploring the ancient wood have uncovered unique fungi and bacteria thriving on the submerged cypress remains.
Some of these microorganisms are previously unknown to science and possess remarkable properties, including the potential to produce novel antibiotics or enzymes.
This discovery opens exciting avenues for biomedical research, as these rare life forms may hold keys to fighting infections or developing new medical treatments.
11. Comparing to Other Submerged Forests

The Alabama underwater forest stands out among submerged forests worldwide, such as the “Doggerland” forests beneath the North Sea.
While similar sites have provided glimpses into prehistoric landscapes, the exceptional preservation of the cypress wood near Alabama is rare.
These global discoveries together enrich our understanding of ancient environments and the dramatic changes brought by shifting seas and climate over millennia.
12. Advanced Technology in Exploration

Researchers have harnessed cutting-edge technology to explore the underwater forest.
Tools like submersibles, sonar mapping systems, and underwater drones allow scientists to precisely map the site, collect samples, and observe fragile structures without causing damage.
These innovations have revolutionized how experts investigate submerged environments, revealing details that would otherwise remain hidden beneath the waves.
13. The Role of Local Fishermen

Local fishermen played a crucial part in the discovery by sharing stories of unusual catches and odd underwater formations in the area.
Their firsthand observations and willingness to collaborate with divers and scientists helped pinpoint the exact location of the submerged forest.
This partnership highlights the value of community knowledge in scientific breakthroughs.
14. Preserving the Forest
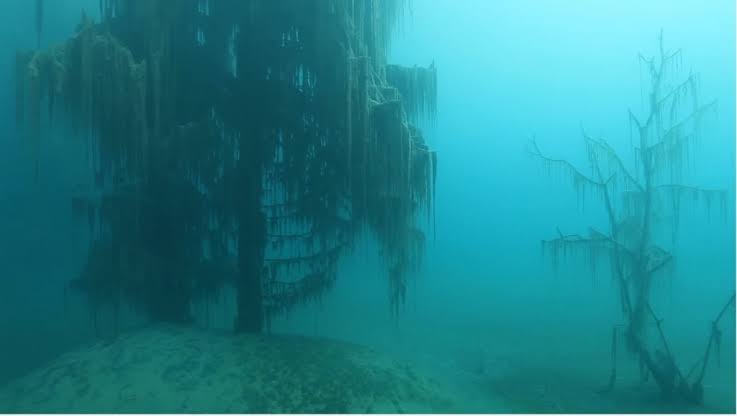

With the forest’s scientific and ecological value now recognized, efforts are underway to protect the site from commercial exploitation and disturbance.
Researchers, conservationists, and local authorities are collaborating to secure legal safeguards and establish responsible protocols for future exploration.
Preserving this underwater treasure ensures that its secrets remain accessible for ongoing research, education, and the benefit of generations yet to come.
15. Insights into Ancient Ecosystems
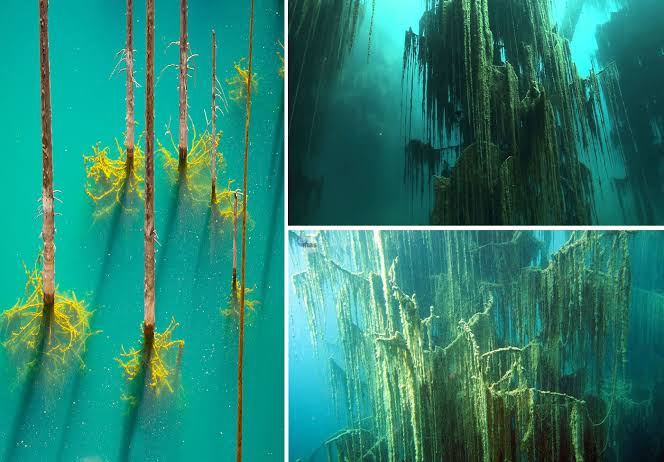

The underwater forest provides a rare glimpse into Gulf Coast ecosystems that existed long before human settlement.
By studying the preserved trees, soils, and remnants of plant and animal life, scientists can reconstruct the landscape’s biodiversity and environmental conditions.
These findings help reveal the natural history of the region and the ways in which ancient ecosystems adapted to changing climates and rising seas.
16. Implications for Sea Level Rise
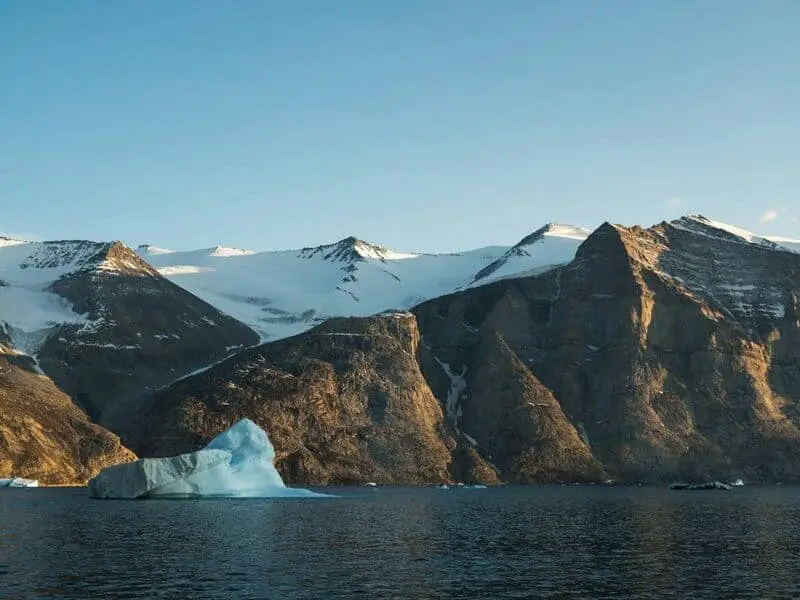

The forest’s submersion offers powerful evidence of dramatic sea level rise since the last ice age.
Studying this site helps scientists understand how rapid environmental changes can transform coastal landscapes.
These lessons are especially relevant today, as modern communities along the Gulf and worldwide face the growing threat of rising seas driven by ongoing climate change.
17. Scientific Publications and Recognition

The discovery has led to a surge of academic papers and mainstream media coverage, dramatically raising the underwater forest’s scientific profile.
Major outlets like National Geographic have featured the site, sparking global interest and collaboration.
These publications ensure ongoing research and broader public appreciation for this extraordinary natural wonder.
18. The Forest’s Size and Scale
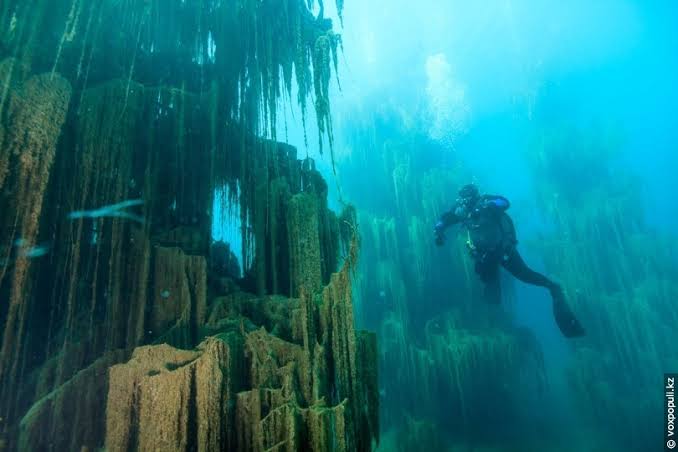

Researchers estimate that the underwater forest spans at least half a square mile beneath the Gulf waters.
This remarkable expanse makes it one of the largest and best-preserved submerged ancient forests ever discovered.
The sheer scale of the site not only adds to its scientific significance but also highlights the vast prehistoric landscapes that once covered the region.
19. Archaeological Significance
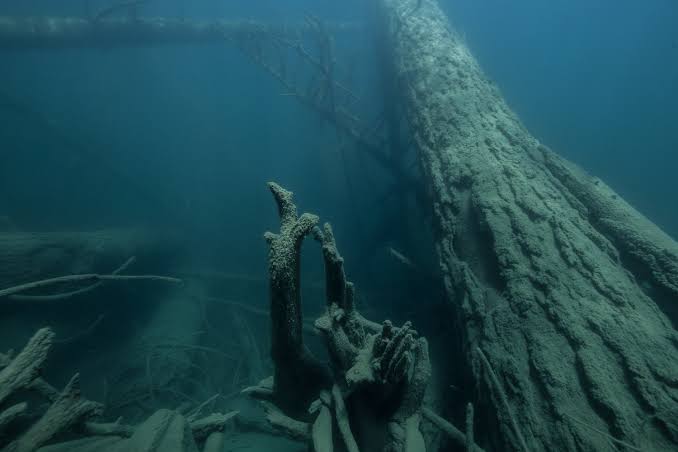

Beyond its ecological value, the underwater forest holds archaeological intrigue.
Researchers speculate that the area might yield traces of early human activity or artifacts, as ancient peoples could have inhabited or traversed this landscape before it was submerged.
Future excavations may yet reveal evidence, linking the site to the broader story of human migration and adaptation in North America.
20. Challenges in Research

Studying the submerged forest is not without obstacles.
Researchers face poor visibility, unpredictable currents, and the constant challenge of protecting sensitive equipment in a marine environment.
These difficulties require careful planning and advanced technology, often limiting direct access to the site and slowing the pace of discovery.
Despite these hurdles, the scientific rewards continue to outweigh the risks.
21. Funding and Support

Ongoing exploration and preservation of the underwater forest depend on grants and institutional backing.
Support from universities, government agencies, and private organizations has been vital for fieldwork, equipment, and conservation efforts.
Continued funding ensures researchers can unlock the forest’s secrets, safeguard its fragile environment, and share discoveries that benefit both science and the wider public.
22. Educational Opportunities

The underwater forest acts as a living classroom for students, educators, and aspiring scientists.
Field trips, research projects, and virtual explorations offer immersive learning experiences in marine biology, geology, and environmental science.
By engaging the next generation, the site inspires curiosity and fosters a deeper appreciation for the hidden wonders and ongoing mysteries of our planet’s oceans.
23. Potential for Future Discoveries

The Alabama underwater forest raises exciting possibilities for future discoveries along the Gulf Coast.
Scientists believe that other submerged forests or ancient landscapes may lie hidden beneath the waves, waiting to be uncovered.
Each new find could further illuminate the region’s prehistoric past and deepen our understanding of how changing climates have shaped coastal environments over millennia.
24. Inspiring Conservation Policies

The underwater forest’s discovery has the power to shape marine conservation and heritage policies far beyond Alabama.
By highlighting the value of hidden underwater ecosystems, the site encourages lawmakers and conservationists to adopt stronger protections for submerged cultural and natural resources.
These insights can inspire broader efforts to safeguard marine environments and preserve our planet’s ancient legacies for future generations.
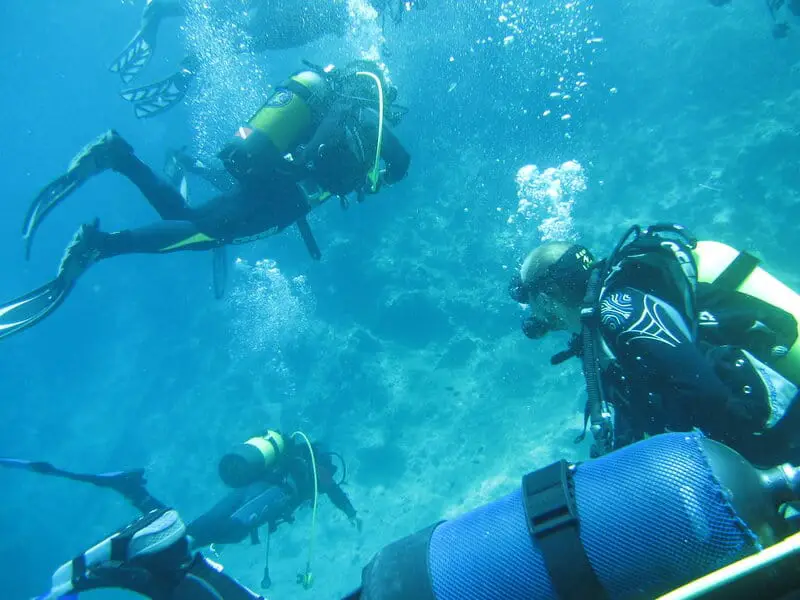
25. A Living Link to the Distant Past

The submerged cypress forest stands as a living link to a vanished world, offering a rare, tangible connection to life before recorded history.
Its silent trunks and preserved roots invite us to imagine the vibrant landscapes and ancient creatures that once thrived there.
This remarkable site reminds us how much of our planet’s story remains hidden, waiting to be rediscovered and understood.
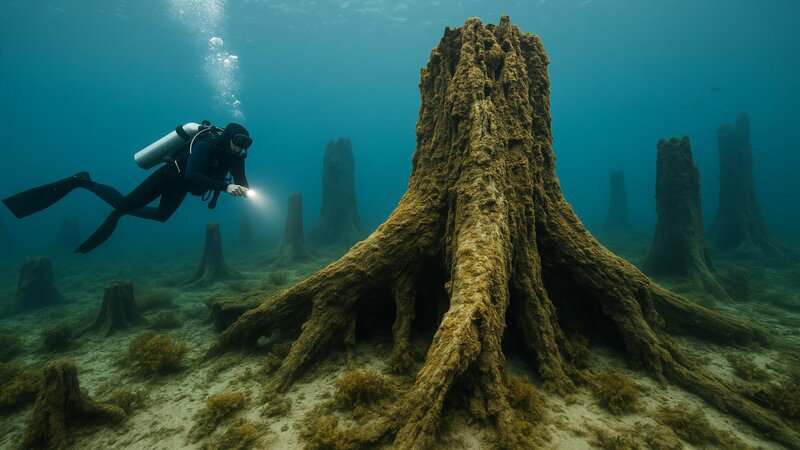
Conclusion

The Alabama underwater forest stands as a testament to the enduring mysteries and resilience of our planet.
Its ancient trees preserve vital clues about prehistoric climates, ecosystems, and even early human activity, while providing a vibrant habitat for modern marine life.
As scientists continue to uncover its secrets, this remarkable site inspires awe and underscores the importance of protecting our natural and cultural heritage.
By supporting ongoing research and conservation, we help ensure that these invaluable windows into our distant past remain accessible for generations to come.



Vielleicht interessiert es Sie:
13 Extraordinary Giants Ready to Blow Your Mind! 🌍
10 Chonky Oddities That Will Leave You Speechless! 🤯
9 Unbelievable Absolute Units That Will Leave You Speechless! 🌟
10 Colossal Creatures That Will Leave You Speechless! 🐻
12 Shocking Absolute Units You’ll Have to See! 😲
12 Epic Absolute Units That Will Challenge Your Perceptions! 🔥
Uncover the 11 Ultimate Massive Oddities That Awe! 🌍
9 Unbelievable Oddities That Redefine ‚Massive‘! 🐉💎