Long-term memory shapes who we are, holding the stories, skills, and emotions that define our lives.
Yet for decades, scientists have puzzled over how our brains preserve memories for years—or even a lifetime.
What secret mechanism allows fleeting moments to become lasting imprints in our minds?
The search for answers has led researchers to a surprising discovery: a protein called KIBRA.
Once obscure, KIBRA is now at the forefront of memory research, promising to reveal how memories endure.
This article explores the remarkable journey from mystery to breakthrough.
1. The Mystery of Long-Term Memory

For years, scientists wondered: How does the brain store information for decades when the proteins inside our neurons are constantly renewed?
This paradox led to a foundational question—could there be special molecules responsible for memory persistence?
Unraveling this enigma inspired generations of research into the biological roots of memory.
Learn more about this mystery.
2. Discovery of KIBRA

In the early 2000s, researchers identified KIBRA as a protein highly expressed in memory-related brain regions.
What set KIBRA apart was its strong correlation with memory performance in humans—a connection confirmed by genetic studies.
Unlike well-known proteins such as CREB, KIBRA’s unique function intrigued scientists.
Its discovery opened new avenues for understanding how we form and retain memories.
Read the original study.
3. KIBRA and Synaptic Plasticity
Synaptic plasticity—the process by which neural connections strengthen or weaken—forms the basis of learning and memory.
KIBRA plays a direct role in regulating this plasticity, influencing how memories are encoded and maintained.
Unlike other synaptic proteins that serve structural roles, KIBRA acts as a dynamic regulator within signaling pathways.
Explore the research.
4. The Role of PKMζ in Memory
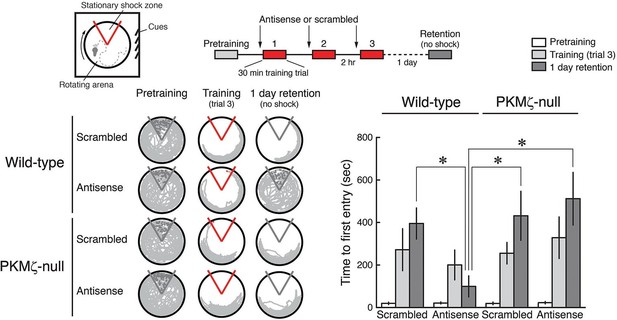
Another key player in memory is PKMζ, an enzyme renowned for its role in sustaining long-term potentiation (LTP)—a process vital for memory storage.
Often dubbed a “memory molecule”, PKMζ helps keep synaptic connections strong long after learning occurs.
Its discovery highlighted the importance of biochemical pathways in making memories last.
See the details here.
5. KIBRA Meets PKMζ: A 2024 Breakthrough

In a major 2024 breakthrough, scientists discovered that KIBRA directly binds to PKMζ, shielding it from cellular mechanisms that degrade proteins.
This crucial interaction finally explains how memories can persist for years—even as brain proteins are constantly replaced.
KIBRA acts as a molecular guardian, ensuring PKMζ remains active and memory traces stay intact.
Read the groundbreaking study.
6. How KIBRA Stabilizes Brain Connections

The KIBRA-PKMζ partnership strengthens synaptic connections by maintaining the molecular “glue” that holds memories in place.
This is similar to immune memory, where specific cells persist to remember past threats.
By ensuring PKMζ’s stability, KIBRA gives our neural circuits the resilience needed for lifelong learning.
Discover the parallels.
7. Implications for Memory Disorders
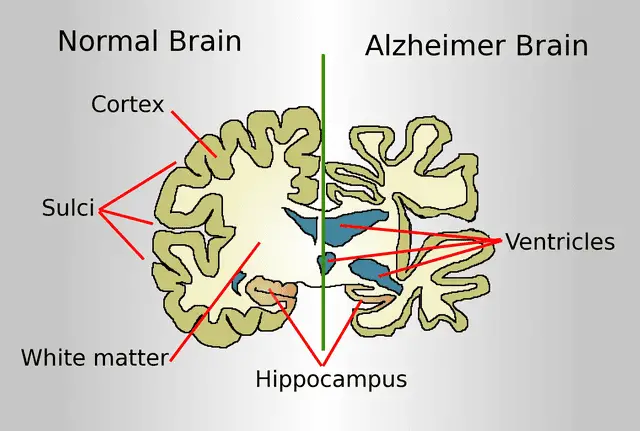
Insights into KIBRA’s function offer hope for tackling memory disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and age-related cognitive decline.
Unlike current treatments that mainly address symptoms, therapies targeting KIBRA could restore or stabilize memory at a molecular level.
This new direction may revolutionize how we approach brain health and memory loss.
Explore KIBRA and Alzheimer’s.
8. Genetic Variations in KIBRA

Not all KIBRA genes are alike—some variants are linked to enhanced memory performance.
Studies reveal that people with certain “memory-boosting” versions of KIBRA excel in memory tasks compared to others.
These genetic differences highlight why memory abilities naturally vary across populations.
See the population studies.
9. KIBRA in Learning and Intelligence
Research shows that individuals with certain KIBRA variants tend to score higher on memory and intelligence assessments.
These results suggest KIBRA’s influence extends beyond memory to broader cognitive abilities, setting it apart from many other genes linked only to intelligence or learning.
KIBRA’s unique impact continues to intrigue scientists exploring the genetic foundation of intellect.
Examine the findings.
10. KIBRA Beyond the Brain
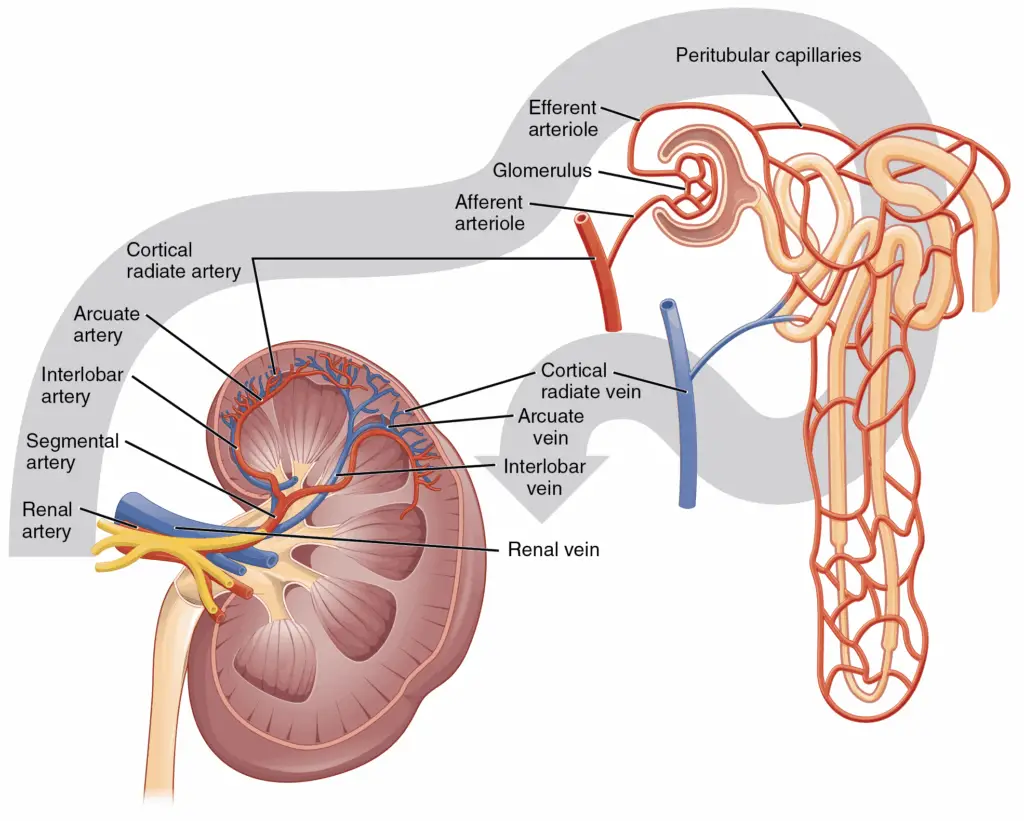
Interestingly, KIBRA isn’t exclusive to the brain—it’s also present in the kidneys and other tissues.
This multi-functional presence echoes other proteins with diverse roles in the body, hinting at KIBRA’s potential importance for overall health.
Its wider functions remain an exciting subject for future research.
Learn about KIBRA’s broader roles.
11. Animal Studies: KIBRA Knockouts

In animal experiments, scientists “knocked out” KIBRA in mice and observed significant memory deficits.
These results mirror other knockout studies targeting learning-related genes, confirming KIBRA’s crucial role in memory retention.
Such research helps clarify how specific proteins underpin complex behaviors.
Review the knockout findings.
12. Measuring KIBRA in the Human Brain
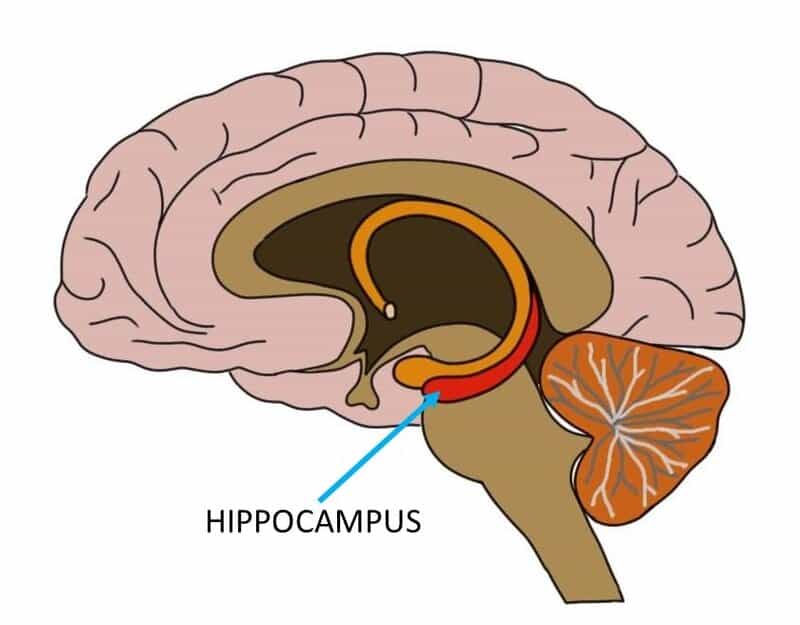
Advanced brain imaging and post-mortem studies have mapped KIBRA expression in key memory regions such as the hippocampus.
Compared to other memory proteins, KIBRA shows particularly strong presence where long-term memories are formed and stored.
These discoveries deepen our understanding of how molecular patterns shape the brain’s memory architecture.
See the mapping studies.
13. KIBRA’s Role in Memory Formation vs. Retrieval
Research indicates that KIBRA is especially important for forming new memories, rather than retrieving old ones.
While other proteins are more involved in recall, KIBRA’s primary action helps encode and stabilize fresh experiences.
This distinction sheds light on the specialized molecular machinery behind different memory processes.
Read more on memory phases.
14. Potential for Memory Enhancement

With KIBRA’s central role in memory, scientists are exploring ways to enhance its function using drugs or gene therapies.
Early research hints at the possibility of boosting memory for those with cognitive impairments, or even healthy individuals.
Still, ethical considerations—echoing past debates over cognitive enhancers—must be addressed as these technologies advance.
Examine the ethical debate.
15. KIBRA, Sleep, and Memory Consolidation
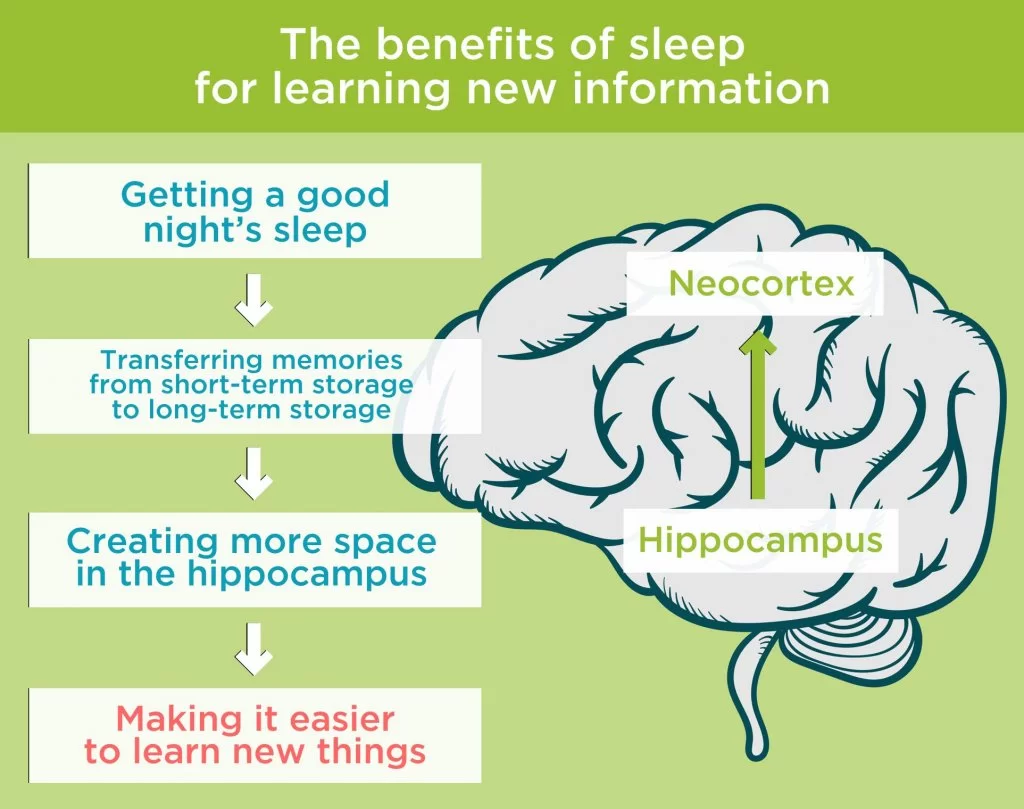
Recent research links KIBRA activity to the brain’s process of solidifying memories during sleep.
While many proteins are involved in sleep-related brain function, KIBRA appears to play a unique role in consolidating new information overnight.
This finding highlights how sleep and memory are molecularly intertwined.
Explore the sleep connection.
16. Age-Related Changes in KIBRA

Studies suggest that KIBRA levels and function may decrease as we age, which could help explain the common decline in memory seen in older adults.
This pattern mirrors changes in other age-sensitive proteins within the brain.
Understanding these shifts may open new avenues for interventions to preserve cognitive health.
Read about age and KIBRA.
17. KIBRA in Childhood and Development

During childhood, KIBRA helps shape the developing brain, potentially laying the groundwork for memory abilities that last a lifetime.
Developmental neuroscience studies suggest that early KIBRA expression may influence how effectively children learn and form lasting memories.
Its role in brain maturation remains a vibrant area of research.
Explore developmental studies.
18. KIBRA and Emotional Memory

Intriguing research suggests that KIBRA may play a heightened role in storing emotional memories—the vivid recollections tied to impactful life events.
This function is similar to proteins found in the amygdala, the brain’s emotion center.
KIBRA’s influence on emotional learning highlights its broad importance across many memory types.
Learn more about emotion and memory.
19. Links to Creativity and Problem Solving

Early studies indicate that KIBRA may also support creative thinking and flexible problem solving, traits often linked to cognitive flexibility.
Compared to other genetic markers of adaptability, KIBRA’s influence appears particularly intriguing, suggesting its effects reach beyond memory into broader aspects of mental agility.
See the creativity research.
20. KIBRA and Stress Resilience

Recent findings suggest that KIBRA may help buffer the negative impacts of stress on memory, offering resilience where other proteins, such as cortisol, can be detrimental.
This protective role distinguishes KIBRA as more than a memory molecule—it’s also a potential ally against stress-related memory decline.
Read about stress and memory.
21. The Future of KIBRA Research

The next decade promises exciting advances in KIBRA research, spanning novel memory-boosting therapies and breakthroughs in personalized medicine.
As scientists unravel the protein’s complex functions, we may see milestones rivaling earlier discoveries in memory science.
Targeted interventions based on individual KIBRA profiles could revolutionize cognitive health for people of all ages.
Explore future directions.
Conclusion

The 2024 discovery of KIBRA’s partnership with PKMζ marks a major leap in our understanding of why some memories last a lifetime.
This breakthrough not only unravels the molecular secret behind memory persistence but also paves the way for future therapies and brain health strategies.
To support your own memory, focus on good sleep, stress management, and lifelong learning.


Vielleicht interessiert es Sie:
13 Extraordinary Giants Ready to Blow Your Mind! 🌍
10 Chonky Oddities That Will Leave You Speechless! 🤯
9 Unbelievable Absolute Units That Will Leave You Speechless! 🌟
10 Colossal Creatures That Will Leave You Speechless! 🐻
12 Shocking Absolute Units You’ll Have to See! 😲
12 Epic Absolute Units That Will Challenge Your Perceptions! 🔥
Uncover the 11 Ultimate Massive Oddities That Awe! 🌍
9 Unbelievable Oddities That Redefine ‚Massive‘! 🐉💎