Recent scientific research has unveiled a remarkable discovery: a common vitamin, once overlooked, is now recognized as a powerful ally in accelerating wound healing. This unexpected breakthrough is sending ripples through the medical community, shining a spotlight on the vital role nutrition can play in recovery. Imagine faster healing times and improved outcomes for millions facing injuries, surgeries, or chronic wounds. As experts dig deeper into the mechanisms behind this vitamin’s healing magic, the potential to revolutionize both medicine and personal health routines has never been clearer.
1. The Rockefeller University Breakthrough

In 2024, scientists at The Rockefeller University made headlines by revealing Vitamin A’s pivotal role in wound repair. Their research highlighted how hair follicle stem cells harness retinoic acid—an active form of Vitamin A—to orchestrate tissue regeneration.
This discovery not only clarified why wounds sometimes heal poorly, but also opened the door to innovative therapies targeting the body’s natural repair mechanisms.
2. Understanding Vitamin A

Vitamin A is a fat-soluble nutrient essential for vision, immune function, and cellular communication.
It exists mainly as retinol in animal sources and beta-carotene in plants. Traditionally, its importance has centered on eye health and immunity.
Now, with its emerging role in tissue repair, Vitamin A’s impact on our well-being is being redefined in exciting ways.
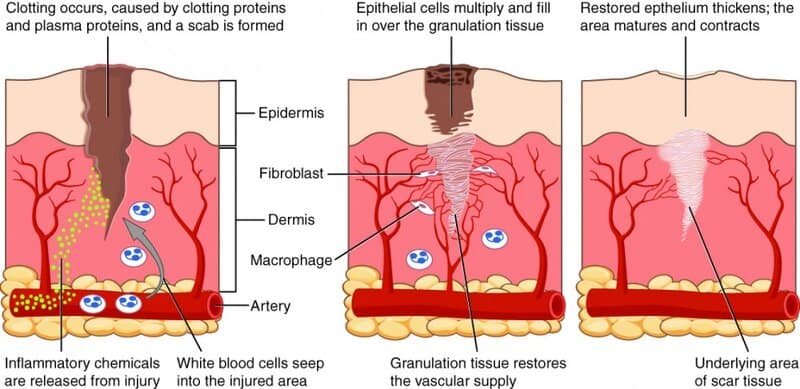
3. How Wound Healing Works
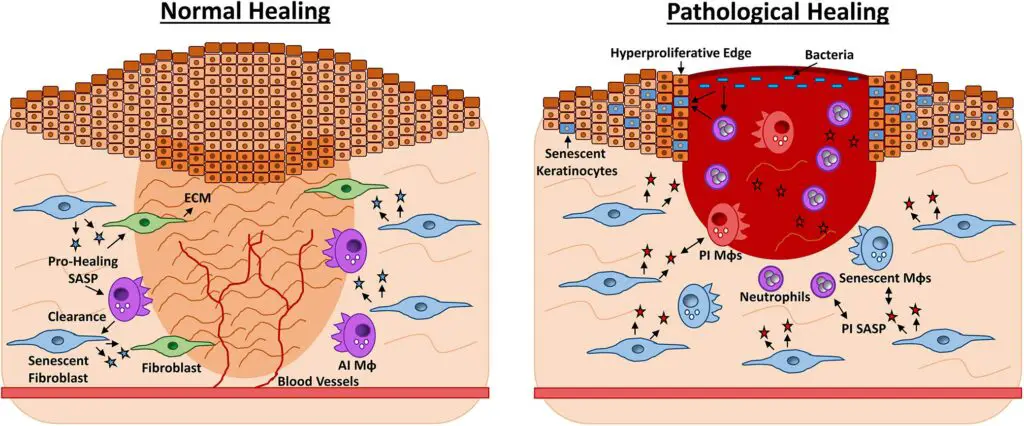
Wound healing unfolds in distinct stages: inflammation, tissue formation, and remodeling.
Cells rush to the site, control bleeding, fight infection, and rebuild new tissue.
Faster, more efficient healing reduces the risk of complications like infection or scarring.
This is why discoveries that improve these natural processes—such as Vitamin A’s influence—can dramatically enhance medical outcomes and patient recovery.
4. The Role of Hair Follicle Stem Cells
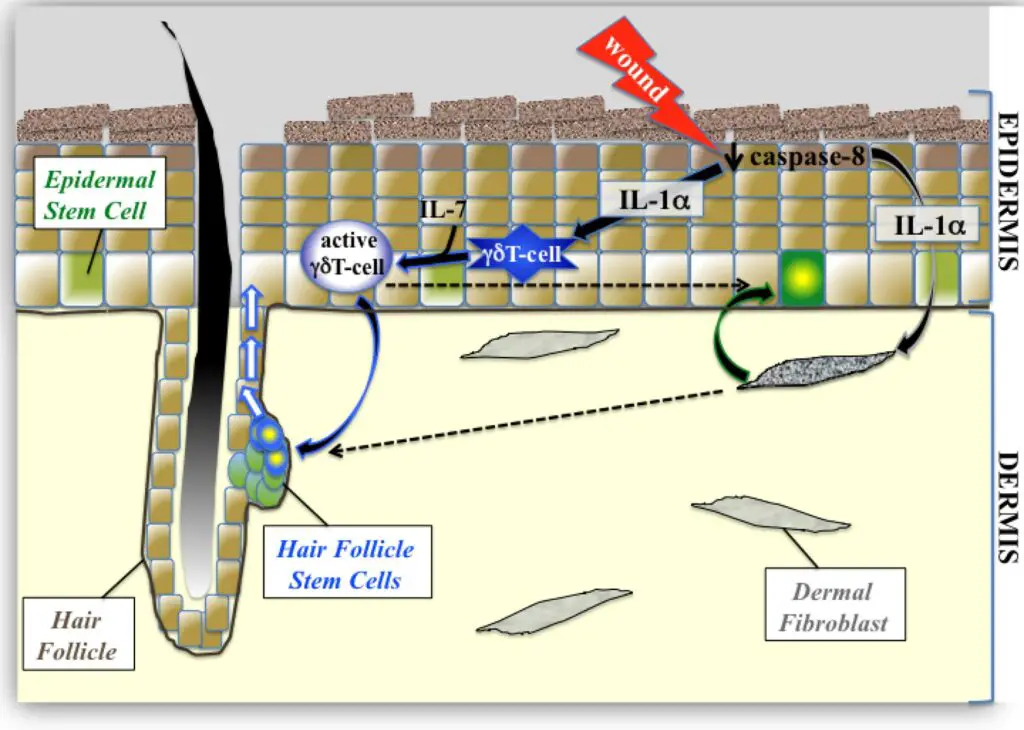
Scientists have discovered that hair follicle stem cells are not just responsible for hair growth—they also play a central role in skin regeneration.
When the skin is injured, these specialized cells migrate to the wound and help form new tissue.
This revelation has transformed our understanding of wound repair, showing that the skin’s own resources, guided by nutrients like Vitamin A, are crucial for effective healing.
5. Retinoic Acid: The Key Mediator
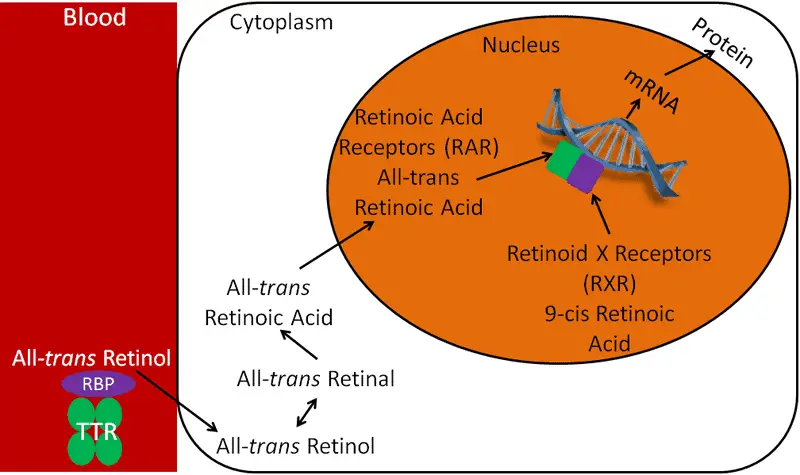
Retinoic acid is a biologically active form of Vitamin A that acts as a potent signaling molecule within our cells.
After Vitamin A is consumed, the body converts it into retinoic acid, which then communicates with stem cells—especially those from hair follicles.
This signal prompts the cells to mobilize and rapidly close wounds, making retinoic acid an essential player in the body’s regenerative toolkit.
6. Vitamin A vs. Other Vitamins

While Vitamin C supports collagen synthesis and Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant, Vitamin A stands out for its direct influence on stem cell behavior and tissue regeneration.
Unlike other vitamins, its ability to create retinoic acid uniquely drives the cellular signals needed for rapid wound closure, giving it a distinct and powerful role in healing.
7. Evidence from Clinical Studies

Recent clinical studies have provided compelling evidence for Vitamin A supplementation in wound care.
Patients receiving controlled doses of Vitamin A showed faster healing times, improved tissue strength, and fewer complications compared to those without supplementation.
These results have been observed in both surgical and chronic wound cases, reinforcing the vitamin’s critical impact.
As research continues, experts are optimistic about integrating Vitamin A more widely into medical protocols.
8. Implications for Chronic Wounds
Vitamin A’s ability to activate stem cells and accelerate healing brings new hope for patients with chronic wounds, such as diabetic ulcers.
Traditional treatments often struggle with these stubborn injuries.
Emerging Vitamin A therapies may offer a breakthrough—promoting tissue regeneration where standard care has failed and potentially reducing the risks of infection and long-term disability.
9. Nutritional Sources of Vitamin A

You can boost your Vitamin A intake through foods like liver, eggs, dairy products, carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens.
A balanced diet rich in these sources supports not only vision and immunity, but also skin integrity and wound healing.
Smart dietary choices can make a meaningful difference in your body’s ability to recover from injuries.
10. Topical vs. Oral Vitamin A

Vitamin A can benefit wound healing when applied topically or taken orally.
Topical treatments deliver retinoic acid directly to the skin, often accelerating local repair.
Oral intake—via diet or supplements—supports the body’s overall healing capacity.
Each approach has unique advantages, and combining them may offer the most comprehensive support for skin regeneration and faster recovery.
11. Safety and Dosage Considerations

While Vitamin A is essential for healing, it’s crucial to use it safely.
Recommended daily allowances vary by age and gender, but excessive intake can cause toxicity—manifesting as headaches, liver issues, or skin changes.
Consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements, especially for wound healing purposes.
Proper dosing ensures you harness the benefits without risking adverse effects or interactions with other medications.
12. Real-Life Healing Stories
Across the globe, individuals have experienced remarkable recoveries thanks to Vitamin A-based treatments.
For example, a diabetic patient with a persistent ulcer saw rapid improvement after adding Vitamin A supplements.
Others report faster post-surgical healing and less scarring.
These stories highlight the practical, life-changing potential of this vitamin in everyday wound care.
13. Applications in Surgery and Trauma
Surgeons and trauma specialists are exploring Vitamin A to enhance recovery from incisions and injuries.
Supplementing or applying Vitamin A may speed healing, minimize infection risk, and reduce scarring after operations or accidents.
This approach could mark a significant advance in post-surgical care and emergency medicine, improving outcomes for countless patients.
14. Impact on Aging Skin

As skin ages, its ability to heal and regenerate diminishes.
Vitamin A offers powerful anti-aging benefits by stimulating collagen production and enhancing wound repair, even in older adults.
Regular use—whether in diet or topical creams—can reduce scarring, improve skin texture, and promote a more youthful appearance, making it invaluable for aging skin health.
15. Potential for Burn Treatment
Researchers are actively investigating Vitamin A as a promising therapy for burn victims.
Early studies suggest that Vitamin A may not only accelerate skin regeneration but also help minimize long-term scarring.
This innovative approach could profoundly improve the recovery process for those suffering from severe burns, offering renewed hope and better outcomes.
16. Veterinary Medicine Insights

Vitamin A’s healing powers aren’t just for humans—animal studies and veterinary care have shown remarkable results as well.
Pets and livestock treated with Vitamin A supplements or ointments often experience faster recovery and healthier skin after injuries.
These findings further reinforce the vitamin’s universal role in tissue repair across species.
17. Innovations in Skin Care Products

The cosmetic industry has eagerly embraced Vitamin A derivatives, such as retinol and retinoids, in advanced skin care products.
These formulations are celebrated for their ability to stimulate skin renewal, fade discolorations, and promote faster healing of minor blemishes.
As research grows, consumers are increasingly turning to these products for both aesthetic improvements and enhanced skin health.
18. Addressing Vitamin A Deficiency

A deficiency in Vitamin A can significantly impair wound healing and overall skin health.
Populations at risk—such as children, pregnant women, and those with limited diets—should focus on nutrient-rich foods or safe supplementation.
Regular health screenings and public health initiatives are essential strategies to prevent deficiency and ensure optimal healing potential for everyone.
19. Future Research Directions

The future of Vitamin A in wound healing looks promising, with researchers exploring targeted stem cell therapies and personalized approaches to optimize recovery.
Innovations may include custom-tailored Vitamin A treatments based on genetic profiles and advanced delivery systems.
These breakthroughs could transform wound care, offering even more effective and individualized solutions for patients worldwide.
20. Myths and Misconceptions

Despite growing evidence, myths persist about Vitamin A.
It’s important to note that more is not always better—excessive doses can be harmful.
Current science supports its role in healing, but not as a miracle cure for all wounds.
Always rely on medical guidance and evidence-based sources for safe, effective use.
21. How to Discuss Vitamin A with Your Doctor

When considering Vitamin A for wound healing, prepare questions and share your medical history with your doctor.
Ask about safe dosages, possible interactions, and whether topical or oral forms are best for your needs.
Open communication ensures you receive personalized, evidence-based advice tailored to your unique health situation.
Conclusion
The Rockefeller University discovery has cast Vitamin A in a new light—as a vital catalyst for wound healing and skin regeneration.
From activating stem cells to supporting chronic wound care, the evidence is compelling.
This breakthrough invites us to rethink nutrition and medical care, yet always with expert guidance.
As research advances, Vitamin A’s promise continues to grow—offering hope for swifter recovery and healthier skin for all.
Disclaimer

This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes to your health regimen or starting new supplements.


Vielleicht interessiert es Sie:
13 Extraordinary Giants Ready to Blow Your Mind! 🌍
10 Chonky Oddities That Will Leave You Speechless! 🤯
9 Unbelievable Absolute Units That Will Leave You Speechless! 🌟
10 Colossal Creatures That Will Leave You Speechless! 🐻
12 Shocking Absolute Units You’ll Have to See! 😲
12 Epic Absolute Units That Will Challenge Your Perceptions! 🔥
Uncover the 11 Ultimate Massive Oddities That Awe! 🌍
9 Unbelievable Oddities That Redefine ‚Massive‘! 🐉💎