Every day, we type passwords, personal messages, and private data without a second thought. It feels safe—after all, what could be more routine? But what if the simple sound of your keyboard could give away your secrets? In a world where cybercriminals are always innovating, even the subtle clicks and clacks of your typing have become a potential goldmine. Recent advances have made it possible for attackers to eavesdrop on keystrokes using only sound, exposing a vulnerability hiding in plain sight.
The Science Behind Acoustic Eavesdropping

When you press a key, it doesn’t just register a character—it creates a distinct sound. Each key on your keyboard has a unique acoustic signature, shaped by its position and the force of your touch. Researchers have shown that machine learning algorithms can analyze these sounds, matching them to individual letters or numbers. As microphones become more sensitive and software more sophisticated, decoding what you type through sound alone is no longer science fiction.
Smartphone and Laptop Microphones as Spying Tools

Cybercriminals don’t need a sophisticated setup to eavesdrop—they can exploit the microphones built into your everyday devices. Malware can secretly activate a smartphone or laptop mic, capturing the sounds of your typing from across the room. In several documented cases, attackers have used malicious software to turn trusted devices into covert surveillance tools. Even a muted or idle phone on your desk could be quietly recording, turning convenience into a hidden threat.
AI and Deep Learning Make Attacks Easier

Artificial intelligence has revolutionized acoustic eavesdropping. Modern deep learning models can filter out background noise and pinpoint the subtle differences between keystroke sounds. Recent studies, like one from Cambridge University, demonstrate AI’s ability to identify passwords with up to 95% accuracy—even in bustling public spaces. These breakthroughs mean attackers need less time, less data, and less pristine conditions to crack your secrets, making the threat more real than ever.
Public Spaces: The Perfect Hunting Ground

Cafes, libraries, and airports are prime targets for acoustic eavesdropping. In these public places, people often type passwords and sensitive messages without thinking twice, surrounded by strangers and background noise. Attackers can simply sit nearby with a compromised smartphone or laptop, blending in while capturing keystroke sounds. There have been documented incidents of cybercriminals recording keystrokes in coffee shops and shared workspaces, proving that even a casual setting can become a digital danger zone.
Passwords and PINs Are Especially Vulnerable

Short, predictable passwords and numeric PINs are low-hanging fruit for audio-based attacks.
Attackers can quickly narrow down possibilities because common choices—like “123456” or “password”—have distinct, easy-to-match sound patterns.
Studies reveal that simple credentials are cracked with far higher accuracy than longer, complex passphrases.
Randomized strings with varied characters generate more diverse acoustic signatures, significantly lowering an attacker’s success rate and making brute-force attempts much harder.
Hardware Differences: Mechanical vs. Membrane Keyboards
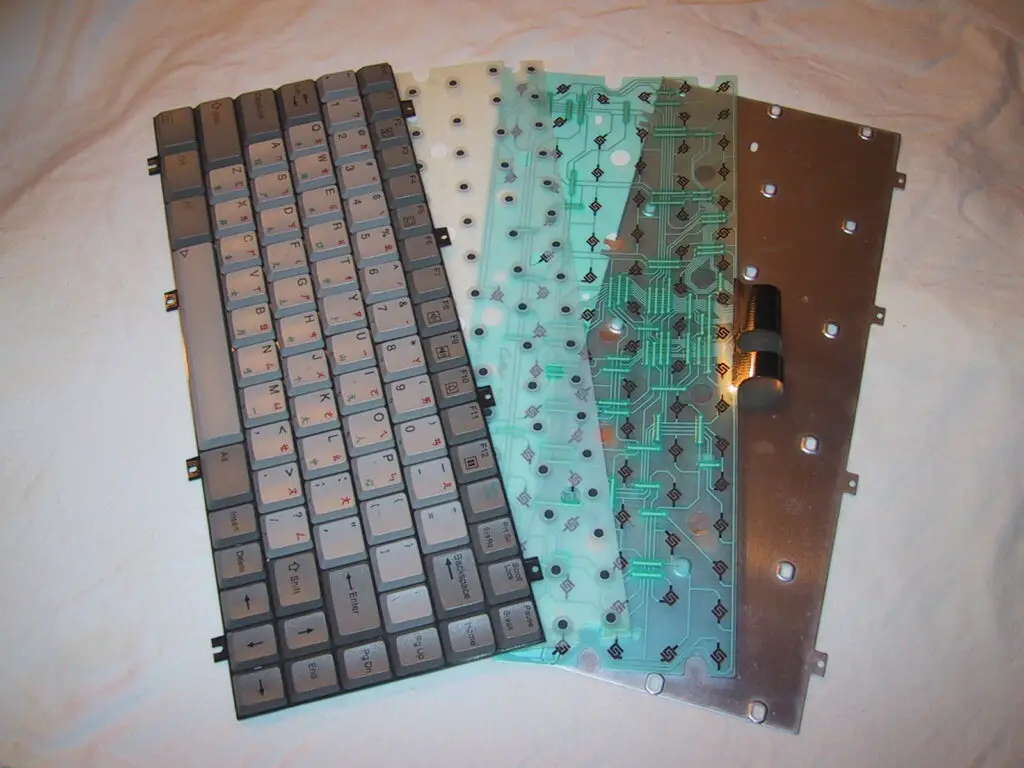

Not all keyboards are equally at risk. Mechanical keyboards produce louder, more distinctive clicks, making it easier for attackers to identify each key’s sound.
In contrast, membrane keyboards—common on many laptops—generate softer, less varied noises, posing a bigger challenge for acoustic analysis.
A study by USENIX found that mechanical models are up to 20% more vulnerable to sound-based attacks.
Your choice of hardware can play a surprising role in your online security.
Keylogging vs. Acoustic Attacks: A Silent Evolution

Traditional keyloggers capture keystrokes by infecting your system with malicious software, but audio-based attacks take a stealthier approach.
Since they only require access to a microphone, these attacks can slip past most antivirus and endpoint security tools unnoticed.
Cybersecurity advisories now warn that this “side-channel” method is rapidly evolving.
Unlike conventional malware, acoustic eavesdropping leaves few digital traces, making detection and prevention far more challenging.
Eavesdropping at a Distance
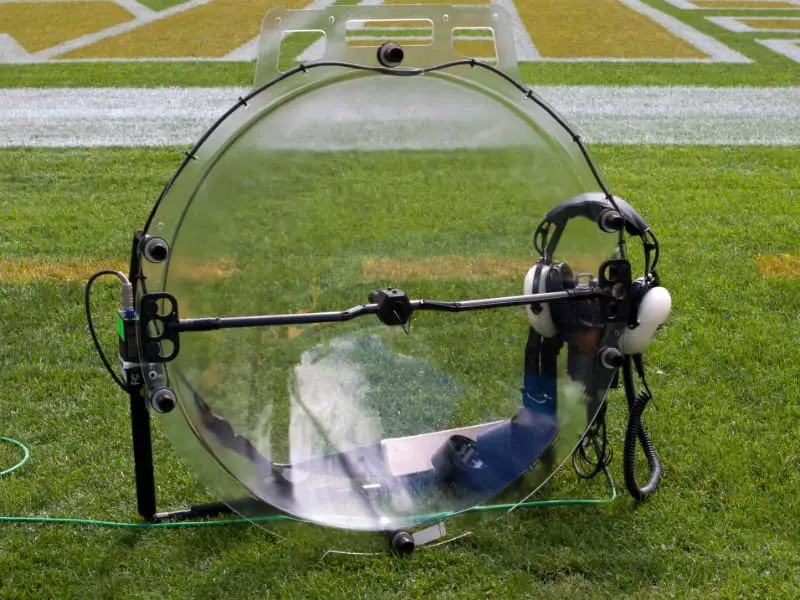

The threat isn’t limited to devices on your desk—sensitive microphones can pick up keystroke sounds from across a room or even through barriers.
Investigative reports have shown attackers using directional microphones to record typing from several meters away, sometimes even through thin walls or windows.
Journalists at Wired and The Guardian have demonstrated how easily sound can travel and be intercepted, highlighting just how vulnerable we can be—even when we think we’re alone.
Countermeasures: How to Protect Yourself

You’re not defenseless against acoustic attacks. Simple steps can make a big difference: use on-screen keyboards for entering sensitive data, or play background noise to mask your keystrokes.
Consider switching to quieter, less distinctive keyboards if possible.
Regularly check device permissions to ensure microphones aren’t being accessed unexpectedly.
For more tips, visit these cybersecurity resources:
Cyber Aware (UK Government)CISA: Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency
Corporate Espionage: When Businesses Become Targets

Corporate environments present lucrative targets for acoustic eavesdropping attacks, where sensitive business information, trade secrets, and financial data are regularly typed. Industrial espionage has evolved beyond traditional methods, with competitors and nation-state actors using sophisticated audio surveillance to steal intellectual property. Open office layouts, conference rooms, and shared workspaces amplify the risk, as multiple keyboards create a symphony of potential data leaks.
Virtual Keyboards and Touchscreens: A False Sense of Security

Many users believe virtual keyboards and touchscreens are immune to acoustic attacks, but this assumption is dangerously wrong. Tablets and smartphones still produce subtle sounds when fingers tap the screen, and these acoustic signatures can be analyzed just like physical keystrokes. Recent research has shown that even haptic feedback and slight vibrations from touchscreens can be detected and decoded by sensitive microphones, creating false security.
Typing Patterns: Your Unique Digital Fingerprint

Beyond individual keystrokes, your typing rhythm creates a unique biometric signature that can be used to identify you personally. Attackers can analyze the timing between keystrokes, the duration of key presses, and your natural typing cadence to build a profile of your digital behavior. This “keystroke dynamics” approach allows cybercriminals to not only decode what you type but also determine who is typing, even across different sessions.
Smart Home Devices: Unintended Surveillance Networks

The proliferation of smart home devices has created an unintended network of potential surveillance tools for acoustic eavesdropping. Smart speakers, security cameras, and IoT devices equipped with microphones can inadvertently capture and transmit keystroke sounds to remote servers. Voice assistants that are always listening may process keyboard sounds as ambient noise, but this data could potentially be accessed by sophisticated attackers seeking entry points.
Mobile Keyboards: The Forgotten Vulnerability

Mobile device keyboards present unique challenges for acoustic eavesdropping, with different attack vectors than traditional computers. Swipe typing, predictive text, and auto-correction features create distinct sound patterns that can reveal not just what you type, but how you type. The portability of mobile devices means sensitive typing often occurs in compromised environments where recording devices are easily concealed, making personal communications attractive targets.
Two-Factor Authentication: Not Always a Shield
Two-factor authentication codes, despite being temporary, are still vulnerable to acoustic eavesdropping during the brief window when they’re entered. Attackers can combine keystroke audio with other social engineering tactics to bypass multi-factor authentication systems. The rhythmic pattern of entering 6-digit codes creates predictable acoustic signatures that can be easier to decode than complex passwords, compromising even supposedly secure authentication methods.
Legal and Privacy Implications: The Gray Areas

The legal landscape around acoustic eavesdropping remains murky, with laws struggling to keep pace with technological capabilities. In many jurisdictions, recording audio in public spaces is legal, creating loopholes that attackers can exploit for keystroke surveillance. Privacy laws vary significantly between countries, and what constitutes consent for audio recording in ambient sound capture contexts is often unclear, leaving victims with limited recourse.
Detection and Forensics: Fighting Back with Technology

Security researchers are developing sophisticated methods to detect when acoustic eavesdropping attacks are occurring in real-time. Advanced audio analysis tools can identify suspicious patterns in ambient recordings that suggest keystroke surveillance is taking place. Machine learning algorithms are being trained to recognize the acoustic signatures of eavesdropping equipment, creating early warning systems for potential attacks and helping forensic investigators trace sources.
Environmental Acoustics: How Your Surroundings Betray You

The acoustic properties of your environment can either protect you or make you more vulnerable to eavesdropping attacks. Hard surfaces, high ceilings, and minimal furniture create ideal conditions for sound propagation, making keystroke sounds travel further and remain clearer. Carpeted areas, soft furnishings, and background noise can provide natural acoustic camouflage, making it harder for attackers to isolate keyboard sounds and decode sensitive information.
The Psychology of Acoustic Attacks: Exploiting Human Behavior

Acoustic eavesdropping attacks exploit fundamental human psychology and our false sense of security when typing. People tend to type more carelessly in familiar environments, not realizing that comfort zones can become surveillance zones. The invisible nature of sound-based attacks means victims rarely realize they’re being monitored, leading to repeated exposure over time as attackers leverage social psychology to target vulnerable moments.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Acoustic Cyberattacks

As technology advances, acoustic cyberattacks are likely to become more prevalent and harder to detect. Improved microphones, smarter AI, and the increasing number of connected devices all contribute to a growing threat landscape. Staying informed and adapting your security habits will be crucial as attackers refine their techniques. The best defense is proactive awareness—recognizing that even the sounds around you can become targets, and taking steps to stay one step ahead.
Conclusion

Your keyboard—once just a tool—has become a potential source of risk in the digital age.
From the unique sounds of each keystroke to the vulnerability of familiar devices, cybercriminals are finding new ways to steal what matters most.
Staying safe means more than strong passwords; it demands vigilance and a willingness to adapt as threats evolve.



Vielleicht interessiert es Sie:
13 Extraordinary Giants Ready to Blow Your Mind! 🌍
10 Chonky Oddities That Will Leave You Speechless! 🤯
9 Unbelievable Absolute Units That Will Leave You Speechless! 🌟
10 Colossal Creatures That Will Leave You Speechless! 🐻
12 Shocking Absolute Units You’ll Have to See! 😲
12 Epic Absolute Units That Will Challenge Your Perceptions! 🔥
Uncover the 11 Ultimate Massive Oddities That Awe! 🌍
9 Unbelievable Oddities That Redefine ‚Massive‘! 🐉💎